Molecular and Biochemical Evidence of the Toxic Effects of Terbuthylazine and Malathion in Zebrafish
- PMID: 36978570
- PMCID: PMC10044699
- DOI: 10.3390/ani13061029
Molecular and Biochemical Evidence of the Toxic Effects of Terbuthylazine and Malathion in Zebrafish
Abstract
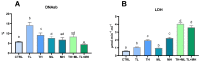
Our research sought to determine the molecular and biochemical effects of environmentally relevant exposure to commonly used chloro-s-triazine herbicide terbuthylazine and organophosphate insecticide malathion on zebrafish. To this aim, mature zebrafish were exposed to 2 and 30 µg L-1 terbuthylazine and 5 and 50 µg L-1 malathion alone and in combination for 14 days. Aside from the accumulation of TBARS and protein carbonyls, a decrease in antioxidants and succinate dehydrogenase activity, an increase in oxidized glutathione, and enhanced apoptosis via Caspase-3 and BAX overexpression were observed. Furthermore, terbuthylazine and malathion induced mitochondrial swelling (up to 210% after single exposure and up to 470% after co-exposure) and lactate dehydrogenase leakage (up to 268% after single exposure and up to 570% after co-exposure) in a concentration-dependent manner. Significant upregulation of ubiquitin expression and increased cathepsin D activity were characteristics that appeared only upon terbuthylazine exposure, whereas the induction of IgM was identified as the specific characteristic of malathion toxicity. Meanwhile, no alterations in the zebrafish hypothalamic-pituitary-thyroid axis was observed. Co-exposure increased the adverse effects of individual pesticides on zebrafish. This study should improve the understanding of the mechanisms of pesticide toxicity that lead to fish impairment and biodiversity decline.
Keywords: Danio rerio; apoptosis; chloro-s-triazine herbicide; cytotoxicity; immune toxicity; organophosphate insecticide; oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Worldometer. Pesticide Use by Country. 2022. [(accessed on 7 July 2022)]. Available online: https://www.worldometers.info/food-agriculture/pesticides-by-country/
-
- FAO Pesticides Use. Global, Regional and Country Trends, 1990–2018. FAOSTAT Analytical Brief Series. No. 16. Rome. 2021. [(accessed on 7 July 2022)]. Available online: https://www.fao.org/3/cb3411en/cb3411en.pdf.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

