H2S Donors with Cytoprotective Effects in Models of MI/R Injury and Chemotherapy-Induced Cardiotoxicity
- PMID: 36978898
- PMCID: PMC10045576
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox12030650
H2S Donors with Cytoprotective Effects in Models of MI/R Injury and Chemotherapy-Induced Cardiotoxicity
Abstract
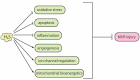
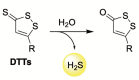
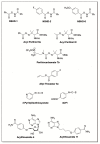
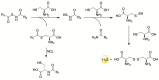
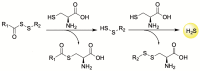
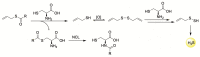
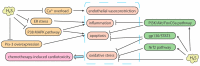
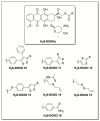
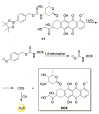
Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) is an endogenous signaling molecule that greatly influences several important (patho)physiological processes related to cardiovascular health and disease, including vasodilation, angiogenesis, inflammation, and cellular redox homeostasis. Consequently, H2S supplementation is an emerging area of interest, especially for the treatment of cardiovascular-related diseases. To fully unlock the medicinal properties of hydrogen sulfide, however, the development and refinement of H2S releasing compounds (or donors) are required to augment its bioavailability and to better mimic its natural enzymatic production. Categorizing donors by the biological stimulus that triggers their H2S release, this review highlights the fundamental chemistry and releasing mechanisms of a range of H2S donors that have exhibited promising protective effects in models of myocardial ischemia-reperfusion (MI/R) injury and cancer chemotherapy-induced cardiotoxicity, specifically. Thus, in addition to serving as important investigative tools that further advance our knowledge and understanding of H2S chemical biology, the compounds highlighted in this review have the potential to serve as vital therapeutic agents for the treatment (or prevention) of various cardiomyopathies.
Keywords: H2S codrugs; H2S donors; MI/R injury; cardioprotection; chemotherapy-induced cardiotoxicity; hydrogen sulfide.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

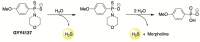

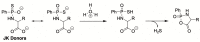

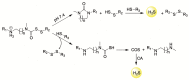

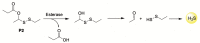
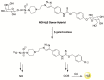
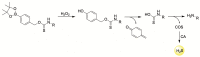

References
-
- Tomlin S. Smelly Cats. Nature. 1998;396:628. doi: 10.1038/25245. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

