Connections between Diabetes Mellitus and Metabolic Syndrome and the Outcome of Cardiac Dysfunctions Diagnosed during the Recovery from COVID-19 in Patients without a Previous History of Cardiovascular Diseases
- PMID: 36979062
- PMCID: PMC10044929
- DOI: 10.3390/biology12030370
Connections between Diabetes Mellitus and Metabolic Syndrome and the Outcome of Cardiac Dysfunctions Diagnosed during the Recovery from COVID-19 in Patients without a Previous History of Cardiovascular Diseases
Abstract
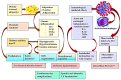
(1) Background: Throughout the COVID-19 pandemic, it became obvious that individuals suffering with obesity, diabetes mellitus (T2DM), and metabolic syndrome (MS) frequently developed persisting cardiovascular complications, which were partially able to explain the onset of the long-COVID-19 syndrome. (2) Methods: Our aim was to document, by transthoracic echocardiography (TTE), the presence of cardiac alterations in 112 patients suffering from post-acute COVID-19 syndrome and T2DM, MS, and/or obesity, in comparison to 91 individuals without metabolic dysfunctions (MD); (3) Results: in patients with MD, TTE borderline/abnormal left (LVF) and/or right ventricular function (RVF), alongside diastolic dysfunction (DD), were more frequently evidenced, when compared to controls (p ˂ 0.001). Statistically significant associations between TTE parameters and the number of factors defining MS, the triglyceride-glucose (TyG) index, the severity of the SARS-CoV-2 infection, and the number of persisting symptoms (p ˂ 0.001) were noted. Significant predictive values for the initial C-reactive protein and TyG index levels, both for the initial and the 6-month follow-up levels of these TTE abnormalities (p ˂ 0.001), were highlighted by means of a multivariate regression analysis. (4) Conclusions: in diabetic patients with MS and/or obesity with comorbid post-acute COVID-19 syndrome, a comprehensive TTE delineates various cardiovascular alterations, when compared with controls. After 6 months, LVF and RVF appeared to normalize, however, the DD-although somewhat improved-did persist in approximately a quarter of patients with MD, possibly due to chronic myocardial changes.
Keywords: COVID-19; diabetes mellitus type 2; diastolic dysfunction; inflammation; insulin resistance syndrome; metabolic syndrome; obesity; transthoracic echocardiography.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

