Origin of Neuroblasts in the Avian Otic Placode and Their Distributions in the Acoustic and Vestibular Ganglia
- PMID: 36979145
- PMCID: PMC10045822
- DOI: 10.3390/biology12030453
Origin of Neuroblasts in the Avian Otic Placode and Their Distributions in the Acoustic and Vestibular Ganglia
Abstract
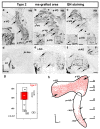
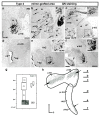
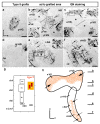
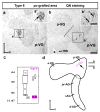
The inner ear is a complex three-dimensional sensorial structure with auditory and vestibular functions. This intricate sensory organ originates from the otic placode, which generates the sensory elements of the membranous labyrinth, as well as all the ganglionic neuronal precursors. How auditory and vestibular neurons establish their fate identities remains to be determined. Their topological origin in the incipient otic placode could provide positional information before they migrate, to later segregate in specific portions of the acoustic and vestibular ganglia. To address this question, transplants of small portions of the avian otic placode were performed according to our previous fate map study, using the quail/chick chimeric graft model. All grafts taking small areas of the neurogenic placodal domain contributed neuroblasts to both acoustic and vestibular ganglia. A differential distribution of otic neurons in the anterior and posterior lobes of the vestibular ganglion, as well as in the proximal, intermediate, and distal portions of the acoustic ganglion, was found. Our results clearly show that, in birds, there does not seem to be a strict segregation of acoustic and vestibular neurons in the incipient otic placode.
Keywords: acoustic ganglion; chick/quail chimaeric embryos; neuroblasts; sensory patch; vestibular ganglion.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Origin of acoustic-vestibular ganglionic neuroblasts in chick embryos and their sensory connections.Brain Struct Funct. 2019 Nov;224(8):2757-2774. doi: 10.1007/s00429-019-01934-5. Epub 2019 Aug 8. Brain Struct Funct. 2019. PMID: 31396696
-
Spatial and temporal segregation of auditory and vestibular neurons in the otic placode.Dev Biol. 2008 Oct 1;322(1):109-20. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2008.07.011. Epub 2008 Jul 19. Dev Biol. 2008. PMID: 18674529
-
Expression of myosin VIIA in the developing chick inner ear neurons.Gene Expr Patterns. 2015 Sep-Nov;19(1-2):36-44. doi: 10.1016/j.gep.2015.07.001. Epub 2015 Jul 23. Gene Expr Patterns. 2015. PMID: 26212629
-
The first steps towards hearing: mechanisms of otic placode induction.Int J Dev Biol. 2007;51(6-7):463-72. doi: 10.1387/ijdb.072320to. Int J Dev Biol. 2007. PMID: 17891709 Review.
-
Signaling regulating inner ear development: cell fate determination, patterning, morphogenesis, and defects.Congenit Anom (Kyoto). 2015 Feb;55(1):17-25. doi: 10.1111/cga.12072. Congenit Anom (Kyoto). 2015. PMID: 25040109 Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

