Insulin Resistance Is Associated with an Unfavorable Serum Lipoprotein Lipid Profile in Women with Newly Diagnosed Gestational Diabetes
- PMID: 36979405
- PMCID: PMC10046655
- DOI: 10.3390/biom13030470
Insulin Resistance Is Associated with an Unfavorable Serum Lipoprotein Lipid Profile in Women with Newly Diagnosed Gestational Diabetes
Abstract
Background: Gestational diabetes (GDM) is associated with various degrees of insulin resistance-a feature related to increased risk of adverse perinatal outcomes. We aimed to determine the previously poorly investigated associations between maternal insulin resistance and serum fasting metabolome at the time of GDM diagnosis.
Methods: Serum lipoprotein and amino acid profile was analyzed in 300 subjects with newly diagnosed GDM using a validated nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy protocol. Associations between insulin resistance (homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance, HOMA2-IR) and serum metabolites were examined with linear regression.
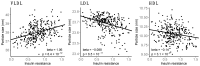
Results: We found insulin resistance to be associated with a distinct lipid pattern: increased concentration of VLDL triglycerides and phospholipids and total triglycerides. VLDL size was positively related and LDL and HDL sizes were inversely related to insulin resistance. Of fatty acids, increased total fatty acids, relative increase in saturated and monounsaturated fatty acids, and relative decrease in polyunsaturated and omega fatty acids were related to maternal insulin resistance.
Conclusions: In newly diagnosed GDM, the association between maternal insulin resistance and serum lipoprotein profile was largely as described in type 2 diabetes. Lifestyle interventions aiming to decrease insulin resistance from early pregnancy could benefit pregnancy outcomes via more advantageous lipid metabolism.
Keywords: GDM; gestational diabetes; insulin resistance; metabolome; metabolomics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Yuen L., Saeedi P., Riaz M., Karuranga S., Divakar H., Levitt N., Yang X., Simmons D. Projections of the Prevalence of Hyperglycaemia in Pregnancy in 2019 and beyond: Results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9th Edition. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2019;157:107841. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2019.107841. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Powe C.E., Allard C., Battista M.C., Doyon M., Bouchard L., Ecker J.L., Perron P., Florez J.C., Thadhani R., Hivert M.F. Heterogeneous Contribution of Insulin Sensitivity and Secretion Defects to Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes Care. 2016;39:1052–1055. doi: 10.2337/dc15-2672. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Immanuel J., Simmons D., Harreiter J., Desoye G., Corcoy R., Adelantado J.M., Devlieger R., Lapolla A., Dalfra M.G., Bertolotto A., et al. Metabolic Phenotypes of Early Gestational Diabetes Mellitus and Their Association with Adverse Pregnancy Outcomes. Diabet. Med. 2021;38:e14413. doi: 10.1111/dme.14413. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

