Knocking Down CDKN2A in 3D hiPSC-Derived Brown Adipose Progenitors Potentiates Differentiation, Oxidative Metabolism and Browning Process
- PMID: 36980212
- PMCID: PMC10047013
- DOI: 10.3390/cells12060870
Knocking Down CDKN2A in 3D hiPSC-Derived Brown Adipose Progenitors Potentiates Differentiation, Oxidative Metabolism and Browning Process
Abstract
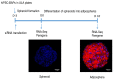
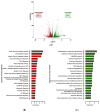
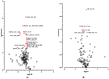
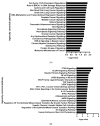
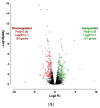
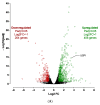
Human induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSCs) have the potential to be differentiated into any cell type, making them a relevant tool for therapeutic purposes such as cell-based therapies. In particular, they show great promise for obesity treatment as they represent an unlimited source of brown/beige adipose progenitors (hiPSC-BAPs). However, the low brown/beige adipocyte differentiation potential in 2D cultures represents a strong limitation for clinical use. In adipose tissue, besides its cell cycle regulator functions, the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 2A (CDKN2A) locus modulates the commitment of stem cells to the brown-like type fate, mature adipocyte energy metabolism and the browning of adipose tissue. Here, using a new method of hiPSC-BAPs 3D culture, via the formation of an organoid-like structure, we silenced CDKN2A expression during hiPSC-BAP adipogenic differentiation and observed that knocking down CDKN2A potentiates adipogenesis, oxidative metabolism and the browning process, resulting in brown-like adipocytes by promoting UCP1 expression and beiging markers. Our results suggest that modulating CDKN2A levels could be relevant for hiPSC-BAPs cell-based therapies.
Keywords: 3D culture; CDKN2A; UCP1; adipocytes; brown adipose progenitor; browning; human induced pluripotent stem cells; thermogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

