Mucins as Potential Biomarkers for Early Detection of Cancer
- PMID: 36980526
- PMCID: PMC10046558
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers15061640
Mucins as Potential Biomarkers for Early Detection of Cancer
Abstract
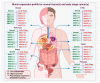
Early detection significantly correlates with improved survival in cancer patients. So far, a limited number of biomarkers have been validated to diagnose cancers at an early stage. Considering the leading cancer types that contribute to more than 50% of deaths in the USA, we discuss the ongoing endeavors toward early detection of lung, breast, ovarian, colon, prostate, liver, and pancreatic cancers to highlight the significance of mucin glycoproteins in cancer diagnosis. As mucin deregulation is one of the earliest events in most epithelial malignancies following oncogenic transformation, these high-molecular-weight glycoproteins are considered potential candidates for biomarker development. The diagnostic potential of mucins is mainly attributed to their deregulated expression, altered glycosylation, splicing, and ability to induce autoantibodies. Secretory and shed mucins are commonly detected in patients' sera, body fluids, and tumor biopsies. For instance, CA125, also called MUC16, is one of the biomarkers implemented for the diagnosis of ovarian cancer and is currently being investigated for other malignancies. Similarly, MUC5AC, a secretory mucin, is a potential biomarker for pancreatic cancer. Moreover, anti-mucin autoantibodies and mucin-packaged exosomes have opened new avenues of biomarker development for early cancer diagnosis. In this review, we discuss the diagnostic potential of mucins in epithelial cancers and provide evidence and a rationale for developing a mucin-based biomarker panel for early cancer detection.
Keywords: autoantibodies; early cancer detection; exosomes; liquid biopsies; mucin biomarker.
Conflict of interest statement
S.K.B. is a co-founder of Sanguine Diagnostics and Therapeutics, Inc. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

