The BAFF-APRIL System in Cancer
- PMID: 36980677
- PMCID: PMC10046288
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers15061791
The BAFF-APRIL System in Cancer
Abstract
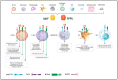
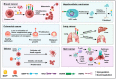
B cell-activating factor (BAFF; also known as CD257, TNFSF13B, BLyS) and a proliferation-inducing ligand (APRIL; also known as CD256, TNFSF13) belong to the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) family. BAFF was initially discovered as a B-cell survival factor, whereas APRIL was first identified as a protein highly expressed in various cancers. These discoveries were followed by over two decades of extensive research effort, which identified overlapping signaling cascades between BAFF and APRIL, controlling immune homeostasis in health and driving pathogenesis in autoimmunity and cancer, the latter being the focus of this review. High levels of BAFF, APRIL, and their receptors have been detected in different cancers and found to be associated with disease severity and treatment response. Here, we have summarized the role of the BAFF-APRIL system in immune cell differentiation and immune tolerance and detailed its pathogenic functions in hematological and solid cancers. We also highlight the emerging therapeutics targeting the BAFF-APRIL system in different cancer types.
Keywords: APRIL; B Cell; BAFF; BAFF-R; BCMA; TACI; hematological cancers; solid cancers.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Roschke V., Sosnovtseva S., Ward C.D., Hong J.S., Smith R., Albert V., Stohl W., Baker K.P., Ullrich S., Nardelli B., et al. BLyS and APRIL form biologically active heterotrimers that are expressed in patients with systemic immune-based rheumatic diseases. J. Immunol. 2002;169:4314–4321. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.169.8.4314. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

