Scoping Review on Epigenetic Mechanisms in Primary Immune Thrombocytopenia
- PMID: 36980827
- PMCID: PMC10048672
- DOI: 10.3390/genes14030555
Scoping Review on Epigenetic Mechanisms in Primary Immune Thrombocytopenia
Abstract
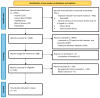
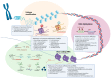
Immune Thrombocytopenia (ITP) is an autoimmune blood disorder that involves multiple pathways responsible for the homeostasis of the immune system. Numerous pieces of literature have proposed the potential of immune-related genes as diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers, which mostly implicate the role of B cells and T cells in the pathogenesis of ITP. However, a more in-depth understanding is required of how these immune-related genes are regulated. Thus, this scoping review aims to collate evidence and further elucidate each possible epigenetics mechanism in the regulation of immunological pathways pertinent to the pathogenesis of ITP. This encompasses DNA methylation, histone modification, and non-coding RNA. A total of 41 studies were scrutinized to further clarify how each of the epigenetics mechanisms is related to the pathogenesis of ITP. Identifying epigenetics mechanisms will provide a new paradigm that may assist in the diagnosis and treatment of immune thrombocytopenia.
Keywords: DNA methylation; autoimmune; blood disorder; epigenetic; histone modification; lncRNA; miRNA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Provan D., Arnold D.M., Bussel J.B., Chong B.H., Cooper N., Gernsheimer T., Ghanima W., Godeau B., González-López T.J., Grainger J., et al. Updated international consensus report on the investigation and management of primary immune thrombocytopenia. Blood Adv. 2019;3:3780–3817. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2019000812. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

