Strategies for Exploiting Milk Protein Properties in Making Films and Coatings for Food Packaging: A Review
- PMID: 36981197
- PMCID: PMC10048563
- DOI: 10.3390/foods12061271
Strategies for Exploiting Milk Protein Properties in Making Films and Coatings for Food Packaging: A Review
Abstract
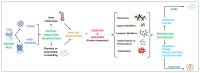
Biopolymers of different natures (carbohydrates, proteins, etc.) recovered from by-products of industrial processes are increasingly being studied to obtain biomaterials as alternatives to conventional plastics, thus contributing to the implementation of a circular economy. The food industry generates huge amounts of by-products and waste, including unsold food products that reach the end of their shelf life and are no longer usable in the food chain. Milk proteins can be easily separated from dairy waste and adapted into effective bio-based polymeric materials. Firstly, this review describes the relevant properties of milk proteins and the approaches to modifying them for subsequent use. Then, we provide an overview of recent studies on the development of films and coatings based on milk proteins and, where available, their applications in food packaging. Comparisons among published studies were made based on the formulation as well as production conditions and technologies. The role of different additives and modifiers tested for the performances of films and coatings, such as water vapor permeability, tensile strength, and elongation at break, were reviewed. This review also outlines the limitations of milk-protein-based materials, such as moisture sensitivity and brittleness. Overall, milk proteins hold great potential as a sustainable alternative to petroleum-based polymers. However, their use in food packaging materials at an industrial level remains problematic.
Keywords: bioplastics; biopolymers; coatings; food packaging; milk proteins; plasticizers; tensile strength; water vapor permeability.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ahmad T., Aadil R.M., Ahmed H., Rahman U.U., Soares B.C., Souza S.L., Pimentel T.C., Scudino H., Guimarães J.T., Esmerino E.A., et al. Treatment and utilization of dairy industrial waste: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019;88:361–372. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2019.04.003. - DOI
-
- Limbo S., Pellegrino L., D’Incecco P., Gobbi S., Rosi V., Fracassetti D. Storage of pasteurized milk in clear PET bottles com-bined with light exposure on a retail display case: A possible strategy to define the shelf life and support a recyclable packaging. Food Chem. 2020;329:127116. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.127116. - DOI - PubMed