Quantum Chaos and Level Dynamics
- PMID: 36981379
- PMCID: PMC10048321
- DOI: 10.3390/e25030491
Quantum Chaos and Level Dynamics
Abstract
We review the application of level dynamics to spectra of quantally chaotic systems. We show that the statistical mechanics approach gives us predictions about level statistics intermediate between integrable and chaotic dynamics. Then we discuss in detail different statistical measures involving level dynamics, such as level avoided-crossing distributions, level slope distributions, or level curvature distributions. We show both the aspects of universality in these distributions and their limitations. We concentrate in some detail on measures imported from the quantum information approach such as the fidelity susceptibility, and more generally, geometric tensor matrix elements. The possible open problems are suggested.
Keywords: 80th birthday of Giulio Casati; level dynamics; quantum chaos.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
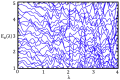
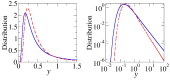
References
-
- Pakoński P., Zakrzewski J. Kepler Map for H Atom Driven by Microwaves with Arbitrary Polarization. Acta Phys. Polon B. 2001;32:2801.
-
- Haake F. Quantum Signatures of Chaos. Springer; Berlin, Germany: 2010.
-
- Stöckmann H. Quantum Chaos: An Introduction. Cambridge University Press; Cambridge, UK: 1999.
-
- Pechukas P. Distribution of Energy Eigenvalues in the Irregular Spectrum. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1983;51:943–946. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.51.943. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

