The Impact of Event Scale-Revised: Examining Its Cutoff Scores among Arab Psychiatric Patients and Healthy Adults within the Context of COVID-19 as a Collective Traumatic Event
- PMID: 36981549
- PMCID: PMC10048280
- DOI: 10.3390/healthcare11060892
The Impact of Event Scale-Revised: Examining Its Cutoff Scores among Arab Psychiatric Patients and Healthy Adults within the Context of COVID-19 as a Collective Traumatic Event
Abstract
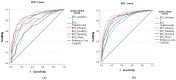
The Impact of Event Scale-Revised (IES-R) is the most popular measure of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). It has been recently validated in Arabic. This instrumental study aimed to determine optimal cutoff scores of the IES-R and its determined six subscales in Arab samples of psychiatric patients (N = 168, 70.8% females) and healthy adults (N = 992, 62.7% females) from Saudi Arabia during the COVID-19 pandemic as a probable ongoing collective traumatic event. Based on a cutoff score of 14 of the Depression Anxiety Stress Scale 8-items (DASS-8), receiver operator curve (ROC) analysis revealed two optimal points of 39.5 and 30.5 for the IES-R in the samples (area under the curve (AUC) = 0.86 & 0.91, p values = 0.001, 95% CI: 0.80-0.92 & 0.87-0.94, sensitivity = 0.85 & 0.87, specificity = 0.73 & 0.83, Youden index = 0.58 & 0.70, respectively). Different cutoffs were detected for the six subscales of the IES-R, with numbing and avoidance expressing the lowest predictivity for distress. Meanwhile, hyperarousal followed by pandemic-related irritability expressed a stronger predictive capacity for distress than all subscales in both samples. In path analysis, pandemic-related irritability/dysphoric mood evolved as a direct and indirect effect of key PTSD symptoms (intrusion, hyperarousal, and numbing). The irritability dimension of the IES-R directly predicted the traumatic symptoms of sleep disturbance in both samples while sleep disturbance did not predict irritability. The findings suggest the usefulness of the IES-R at a score of 30.5 for detecting adults prone to trauma related distress, with higher scores needed for screening in psychiatric patients. Various PTSD symptoms may induce dysphoric mood, which represents a considerable burden that may induce circadian misalignment and more noxious psychiatric problems/co-morbidities (e.g., sleep disturbance) in both healthy and diseased groups.
Keywords: Arabic version/Arab/Saudi Arabia; Coronavirus Disease-19/COVID-19; Impact of Event Scale-Revised (IES-R); cutoff point/cutoff score; post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD); psychiatric or mental disorders/patients/the general public/healthy adults; psychometric evaluation/criterion validity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Al-Amer R., Malak M.Z., Burqan H.M.R., Stănculescu E., Nalubega S., Alkhamees A.A., Hendawy A.O., Ali A.M. Emotional Reaction to the First Dose of COVID-19 Vaccine: Postvaccination Decline in Anxiety and Stress among Anxious Individuals and Increase among Individuals with Normal Prevaccination Anxiety Levels. J. Pers. Med. 2022;12:912. doi: 10.3390/jpm12060912. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chew Q.H., Wei K.C., Vasoo S., Chua H.C., Sim K. Narrative synthesis of psychological and coping responses towards emerging infectious disease outbreaks in the general population: Practical considerations for the COVID-19 pandemic. Singap. Med. J. 2020;61:350. doi: 10.11622/smedj.2020046. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

