Mechanochemical Preparation, Solid-State Characterization, and Antimicrobial Performance of Copper and Silver Nitrate Coordination Polymers with L- and DL-Arginine and Histidine
- PMID: 36982258
- PMCID: PMC10049651
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24065180
Mechanochemical Preparation, Solid-State Characterization, and Antimicrobial Performance of Copper and Silver Nitrate Coordination Polymers with L- and DL-Arginine and Histidine
Abstract
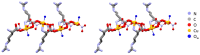
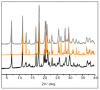
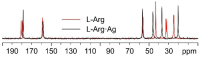
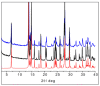
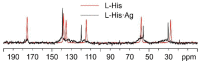
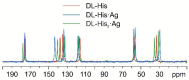
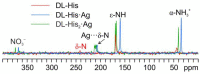
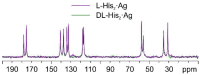
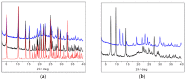
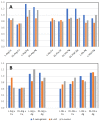
The antimicrobial activity of the novel coordination polymers obtained by co-crystallizing the amino acids arginine or histidine, as both enantiopure L and racemic DL forms, with the salts Cu(NO3)2 and AgNO3 has been investigated to explore the effect of chirality in the cases of enantiopure and racemic forms. The compounds [Cu·AA·(NO3)2]CPs and [Ag·AA·NO3]CPs (AA = L-Arg, DL-Arg, L-His, DL-His) were prepared by mechanochemical, slurry, and solution methods and characterized by X-ray single-crystal and powder diffraction in the cases of the copper coordination polymers, and by powder diffraction and by solid-state NMR spectroscopy in the cases of the silver compounds. The two pairs of coordination polymers, [Cu·L-Arg·(NO3)2·H2O]CP and [Cu·DL-Arg·(NO3)2·H2O]CP, and [Cu·L-Hys·(NO3)2·H2O]CP and [Cu·DL-His·(NO3)2·H2O]CP, have been shown to be isostructural in spite of the different chirality of the amino acid ligands. A similar structural analogy could be established for the silver complexes on the basis of SSNMR. The activity against the bacterial pathogens Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Escherichia coli, and Staphylococcus aureus was assessed by carrying out disk diffusion assays on lysogeny agar media showing that, while there is no significant effect arising from the use of enantiopure or chiral amino acids, the coordination polymers exert an appreciable antimicrobial activity comparable, when not superior, to that of the metal salts alone.
Keywords: amino acids; antimicrobials; co-crystallization; coordination polymers; copper; crystal engineering; mechanochemistry; silver.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Effects of different substituents on the crystal structures and antimicrobial activities of six Ag(I) quinoline compounds.Inorg Chem. 2013 Apr 1;52(7):4046-60. doi: 10.1021/ic400081v. Epub 2013 Mar 4. Inorg Chem. 2013. PMID: 23458224
-
Exploring the Co-Crystallization of Kojic Acid with Silver(I), Copper(II), Zinc(II), and Gallium(III) for Potential Antibacterial Applications.Molecules. 2023 Jan 27;28(3):1244. doi: 10.3390/molecules28031244. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 36770910 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and characterization of water-soluble silver(I) complexes with L-histidine (H2his) and (S)-(-)-2-pyrrolidone-5-carboxylic acid (H2pyrrld) showing a wide spectrum of effective antibacterial and antifungal activities. Crystal structures of chiral helical polymers [Ag(Hhis)]n and ([Ag(Hpyrrld)]2)n in the solid state.Inorg Chem. 2000 Jul 24;39(15):3301-11. doi: 10.1021/ic990526o. Inorg Chem. 2000. PMID: 11196868
-
Bis(amino acidato)copper(II) compounds in blood plasma: a review of computed structural properties and amino acid affinities for Cu2+ informing further pharmacological research.Arh Hig Rada Toksikol. 2024 Sep 29;75(3):159-171. doi: 10.2478/aiht-2024-75-3871. eCollection 2024 Sep 1. Arh Hig Rada Toksikol. 2024. PMID: 39369326 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Silver, Its Salts and Application in Medicine and Pharmacy.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 29;24(21):15723. doi: 10.3390/ijms242115723. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37958707 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Unlocking New Avenues: Solid-State Synthesis of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 18;25(10):5504. doi: 10.3390/ijms25105504. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38791542 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Antimicrobial Resistance. [(accessed on 23 January 2023)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/antimicrobial-resistance.
-
- Antimicrobial Resistance|European Medicines Agency. [(accessed on 23 January 2023)]. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/human-regulatory/overview/public-health-thr....
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

