COVID-19-Induced Myocarditis: Pathophysiological Roles of ACE2 and Toll-like Receptors
- PMID: 36982447
- PMCID: PMC10049267
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24065374
COVID-19-Induced Myocarditis: Pathophysiological Roles of ACE2 and Toll-like Receptors
Abstract
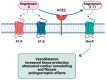
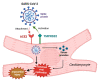
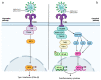
The clinical manifestations of the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection responsible for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) commonly include dyspnoea and fatigue, and they primarily involve the lungs. However, extra-pulmonary organ dysfunctions, particularly affecting the cardiovascular system, have also been observed following COVID-19 infection. In this context, several cardiac complications have been reported, including hypertension, thromboembolism, arrythmia and heart failure, with myocardial injury and myocarditis being the most frequent. These secondary myocardial inflammatory responses appear to be associated with a poorer disease course and increased mortality in patients with severe COVID-19. In addition, numerous episodes of myocarditis have been reported as a complication of COVID-19 mRNA vaccinations, especially in young adult males. Changes in the cell surface expression of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) and direct injury to cardiomyocytes resulting from exaggerated immune responses to COVID-19 are just some of the mechanisms that may explain the pathogenesis of COVID-19-induced myocarditis. Here, we review the pathophysiological mechanisms underlying myocarditis associated with COVID-19 infection, with a particular focus on the involvement of ACE2 and Toll-like receptors (TLRs).
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; Toll-like receptors (TLRs); angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2); cardiovascular system; myocarditis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Richardson P., McKenna W., Bristow M., Maisch B., Mautner B., O’Connell J., Olsen E., Thiene G., Goodwin J., Gyarfas I., et al. Report of the 1995 World Health Organization/International Society and Federation of Cardiology Task Force on the Definition and Classification of cardiomyopathies. Circulation. 1996;93:841–842. - PubMed
-
- Caforio A.L., Pankuweit S., Arbustini E., Basso C., Gimeno-Blanes J., Felix S.B., Fu M., Heliö T., Heymans S., Jahns R., et al. Current state of knowledge on aetiology, diagnosis, management, and therapy of myocarditis: A position statement of the European Society of Cardiology Working Group on Myocardial and Pericardial Diseases. Eur. Heart J. 2013;34:2636–2648, 2648a–2648d. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/eht210. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

