Sinapic Acid Co-Amorphous Systems with Amino Acids for Improved Solubility and Antioxidant Activity
- PMID: 36982605
- PMCID: PMC10053217
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24065533
Sinapic Acid Co-Amorphous Systems with Amino Acids for Improved Solubility and Antioxidant Activity
Abstract
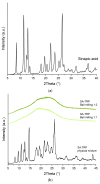
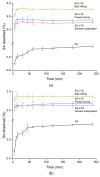
The objective of this study was to obtain co-amorphous systems of poorly soluble sinapic acid using amino acids as co-formers. In order to assess the probability of the interaction of amino acids, namely, arginine, histidine, lysine, tryptophan, and proline, selected as co-formers in the amorphization of sinapic acid, in silico studies were carried out. Sinapic acid systems with amino acids in a molar ratio of 1:1 and 1:2 were obtained using ball milling, solvent evaporation, and freeze drying techniques. X-ray powder diffraction results confirmed the loss of crystallinity of sinapic acid and lysine, regardless of the amorphization technique used, while remaining co-formers produced mixed results. Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy analyses revealed that the co-amorphous sinapic acid systems were stabilized through the creation of intermolecular interactions, particularly hydrogen bonds, and the potential formation of salt. Lysine was selected as the most appropriate co-former to obtain co-amorphous systems of sinapic acid, which inhibited the recrystallization of sinapic acid for a period of six weeks in 30 °C and 50 °C. Obtained co-amorphous systems demonstrated an enhancement in dissolution rate over pure sinapic acid. A solubility study revealed a 12.9-fold improvement in sinapic acid solubility after introducing it into the co-amorphous systems. Moreover, a 2.2-fold and 1.3-fold improvement in antioxidant activity of sinapic acid was observed with respect to the ability to neutralize the 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl radical and to reduce copper ions, respectively.
Keywords: amino acid; co-amorphous; lysine; sinapic acid.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Preparation and characterization of spray-dried co-amorphous drug-amino acid salts.J Pharm Pharmacol. 2016 May;68(5):615-24. doi: 10.1111/jphp.12458. Epub 2015 Aug 5. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26245703
-
Amino acids as co-amorphous excipients for tackling the poor aqueous solubility of valsartan.Pharm Dev Technol. 2017 Feb;22(1):69-76. doi: 10.3109/10837450.2016.1163390. Epub 2016 Apr 6. Pharm Dev Technol. 2017. PMID: 27050301
-
Comparison of co-former performance in co-amorphous formulations: Single amino acids, amino acid physical mixtures, amino acid salts and dipeptides as co-formers.Eur J Pharm Sci. 2021 Jan 1;156:105582. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2020.105582. Epub 2020 Oct 8. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2021. PMID: 33039568
-
[The development of co-amorphous drug systems].Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2013 May;48(5):648-54. Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2013. PMID: 23888685 Review. Chinese.
-
Amorphization of Low Soluble Drug with Amino Acids to Improve Its Therapeutic Efficacy: a State-of-Art-Review.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2023 Dec 7;24(8):253. doi: 10.1208/s12249-023-02709-2. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2023. PMID: 38062314 Review.
Cited by
-
Amorphous Pterostilbene Delivery Systems Preparation-Innovative Approach to Preparation Optimization.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Apr 13;15(4):1231. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15041231. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37111715 Free PMC article.
-
Oleanolic Acid Dimers with Potential Application in Medicine-Design, Synthesis, Physico-Chemical Characteristics, Cytotoxic and Antioxidant Activity.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 26;25(13):6989. doi: 10.3390/ijms25136989. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39000101 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances in Coamorphous Systems of Natural Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients: Preparations, Characterizations, and Applications.ACS Omega. 2025 Aug 5;10(32):35352-35366. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.5c03834. eCollection 2025 Aug 19. ACS Omega. 2025. PMID: 40852262 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Study of Amorphous Kaempferol Dispersions Involving FT-IR Spectroscopy.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 5;24(24):17155. doi: 10.3390/ijms242417155. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38138984 Free PMC article.
-
A drug-drug co-amorphous system for highly improved solubility of breviscapine: an experimental and computational study.Sci Rep. 2024 Dec 28;14(1):31183. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-82524-2. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39732994 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

