Aconitum carmichaelii Debx. Attenuates Heart Failure through Inhibiting Inflammation and Abnormal Vascular Remodeling
- PMID: 36982912
- PMCID: PMC10059042
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24065838
Aconitum carmichaelii Debx. Attenuates Heart Failure through Inhibiting Inflammation and Abnormal Vascular Remodeling
Abstract
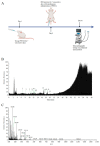
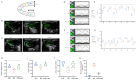
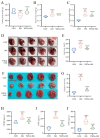
Heart failure (HF) is the most common complication following myocardial infarction, closely associated with ventricular remodeling. Aconitum carmichaelii Debx., a traditional Chinese herb, possesses therapeutic effects on HF and related cardiac diseases. However, its effects and mechanisms on HF-associated cardiac diseases are still unclear. In the present study, a water extraction of toasted Aconitum carmichaelii Debx. (WETA) was verified using UPLC-Q/TOF-MS. The heart function of HF rats was assessed by echocardiography and strain analysis, and myocardial injury was measured by serum levels of CK-MB, cTnT, and cTnI. The pathological changes of cardiac tissues were evaluated by 2,3,5-triphenyltetrazolium chloride (TTC) staining, hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining, and Masson's trichrome staining. Additionally, the levels of inflammation-related genes and proteins and components related to vascular remodeling were detected by RT-qPCR, Western blot, and immunofluorescence. WETA significantly inhibited the changes in echocardiographic parameters and the increase in heart weight, cardiac infarction size, the myonecrosis, edema, and infiltration of inflammatory cells, collagen deposition in heart tissues, and also mitigated the elevated serum levels of CK-MB, cTnT, and cTnI in ISO-induced rats. Additionally, WETA suppressed the expressions of inflammatory genes, including IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α and vascular injury-related genes, such as VCAM1, ICAM1, ANP, BNP, and MHC in heart tissues of ISO-induced HF rats, which were further confirmed by Western blotting and immunofluorescence. In summary, the myocardial protective effect of WETA was conferred through inhibiting inflammatory responses and abnormal vascular remodeling in ISO-treated rats.
Keywords: Aconitum carmichaelii Debx.; Angprotein-2; FOXO1; NF-κB signaling pathway; heart failure; inflammation; vascular remodeling.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Heidenreich P.A., Bozkurt B., Aguilar D., Allen L.A., Byun J.J., Colvin M.M., Deswal A., Drazner M.H., Dunlay S.M., Evers L.R., et al. 2022 AHA/ACC/HFSA Guideline for the Management of Heart Failure: Executive Summary: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2022;145:e876–e894. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000001062. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ezekowitz J.A., O’Meara E., McDonald M.A., Abrams H., Chan M., Ducharme A., Giannetti N., Grzeslo A., Hamilton P.G., Heckman G.A., et al. 2017 Comprehensive Update of the Canadian Cardiovascular Society Guidelines for the Management of Heart Failure. Can. J. Cardiol. 2017;33:1342–1433. doi: 10.1016/j.cjca.2017.08.022. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 82104477/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- U19A2010/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81891012/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2019TQ0044/special support from China Postdoctoral Science Foundation
- No ZYYCXTD-D-202209/Innovation Team and Talents Cultivation Program of National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

