Nivolumab or Atezolizumab in the Second-Line Treatment of Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer? A Prognostic Index Based on Data from Daily Practice
- PMID: 36983409
- PMCID: PMC10053214
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm12062409
Nivolumab or Atezolizumab in the Second-Line Treatment of Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer? A Prognostic Index Based on Data from Daily Practice
Abstract
Background: The efficacy of nivolumab and atezolizumab in advanced pre-treated NSCLC was documented in prospective trials. We aim to confirm the benefits and indicate predictive factors for immunotherapy in daily practice.
Methods: This study was a retrospective analysis. The median PFS and OS were estimated using the Kaplan-Meier method. The log-rank test was used for comparisons. Multivariate analyses were performed using the Cox regression method.
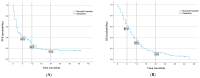
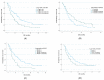
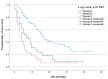
Results: A total of 260 patients (ECOG 0-1) with advanced NSCLC (CS III-IV) were eligible to receive nivolumab or atezolizumab as second-line treatment. Median PFS and OS were three months (95% confidence interval [CI] 2.57-3.42) and 10 months (95% CI 8.03-11.96), respectively, for the overall population. The median OS for the atezolizumab arm was eight months (95% CI 5.89-10.1), while for the nivolumab group, it was 14 months (95% CI 10.02-17.97) (p = 0.018). The sum of all measurable changes >100.5 mm (p = 0.007; HR = 1.003, 95% CI 1.001-1.005), PLT > 281.5 G/l (p < 0.001; HR = 1.003, 95% CI 1.001-1.003) and bone metastases (p < 0.004; HR = 1.58, 95% CI 1.04-2.38) were independent negative prognostic factors for OS in multivariate analysis. Based on preliminary analyses, a prognostic index was constructed to obtain three prognostic groups. Median OS in the subgroups was 16 months (95% CI 13.3-18.7), seven months (95% CI 4.83-9.17) and four months (95% CI 2.88-5.13), respectively (p < 0.001).
Conclusions: Nivolumab and atezolizumab provided clinical benefit in real life. Clinical and laboratory factors may help to identify subgroups likely to benefit. The use of prognostic indices may be valuable in clinical practice.
Keywords: NSCLC; atezolizumab; immunotherapy; nivolumab; prognostic index.
Conflict of interest statement
M.K.-W. Travel expenses and lectures—BMS, MSD, Roche, AstraZeneca, and Takeda; K.W- Lectures—BMS, Roche, and MSD; S.T.- Lectures—BMS, Roche, and MSD, A.P.- Lectures—BMS, Roche, and MSD, K.Z.—Lectures—BMS, Roche, and MSD, M.Z-S. Lectures—BMS, Roche, and MSD; A.P. Travel Expenses and Lectures—BMS, MSD, Roche, and Takeda; D.M.K. Travel Expenses and Advisory Boards—BMS, Roche, AstraZeneca, Amgen, Takeda, and MSD; M.K. Travel Expenses and Advisory Boards—BMS, Roche, AstraZeneca, and Amgen.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Real-World Analysis of Nivolumab and Atezolizumab Efficacy in Previously Treated Patients with Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Apr 25;15(5):533. doi: 10.3390/ph15050533. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35631359 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic immune-inflammation index, neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio can predict clinical outcomes in patients with metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer treated with nivolumab.J Clin Lab Anal. 2019 Oct;33(8):e22964. doi: 10.1002/jcla.22964. Epub 2019 Jul 8. J Clin Lab Anal. 2019. PMID: 31282096 Free PMC article.
-
Real-world effectiveness of immunotherapies in pre-treated, advanced non-small cell lung cancer Patients: A systematic literature review.Lung Cancer. 2022 Apr;166:205-220. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2022.03.008. Epub 2022 Mar 9. Lung Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35316754
-
Efficacy of Atezolizumab for Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Based on Clinical and Molecular Features: A Meta-Analysis.Front Immunol. 2022 Jun 21;13:909027. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.909027. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35799785 Free PMC article.
-
Looking for the best immune-checkpoint inhibitor in pre-treated NSCLC patients: An indirect comparison between nivolumab, pembrolizumab and atezolizumab.Int J Cancer. 2018 Mar 15;142(6):1277-1284. doi: 10.1002/ijc.31136. Epub 2017 Nov 14. Int J Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29080213 Review.
Cited by
-
Prognosis stratification of cancer patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors through lung immune prognostic index: a meta-analysis and systematic review.BMC Cancer. 2024 Apr 25;24(1):523. doi: 10.1186/s12885-024-12271-0. BMC Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38664760 Free PMC article.
-
Immunotherapy for lung adenocarcinoma patients with bone metastases: who really needs it.Front Immunol. 2024 Dec 13;15:1457916. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1457916. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39735542 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic significance of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR) in second-line immunotherapy for patients with non-small cell lung cancer.Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2025 Mar 31;14(3):749-760. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-24-675. Epub 2025 Mar 18. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 40248735 Free PMC article.
-
Atezolizumab Monotherapy for Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Patients: An Observational Study in Ibaraki Group (ATTENTION-IBARAKI).In Vivo. 2023 Sep-Oct;37(5):2203-2209. doi: 10.21873/invivo.13320. In Vivo. 2023. PMID: 37652502 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Borghaei H., Gettinger S., Vokes E.E., Chow L.Q.M., Burgio M.A., de Castro Carpeno J., Pluzanski A., Arrieta O., Frontera O.A., Chiari R., et al. Five-Year Outcomes From the Randomized, Phase III Trials CheckMate 017 and 057: Nivolumab Versus Docetaxel in Previously Treated Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021;39:723–733. doi: 10.1200/JCO.20.01605. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rittmeyer A., Barlesi F., Waterkamp D., Park K., Ciardiello F., von Pawel J., Gadgeel S.M., Hida T., Kowalski D.M., Dols M.C., et al. Atezolizumab versus docetaxel in patients with previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer (OAK): A phase 3, open-label, multicentre randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2017;389:255–265. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)32517-X. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mazieres J., Rittmeyer A., Gadgeel S., Hida T., Gandara D.R., Cortinovis D.L., Barlesi F., Yu W., Matheny C., Ballinger M., et al. Atezolizumab Versus Docetaxel in Pretreated Patients With NSCLC: Final Results From the Randomized Phase 2 POPLAR and Phase 3 OAK Clinical Trials. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2021;16:140–150. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2020.09.022. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

