First-in-Human Integrated Use of a Dedicated Microsurgical Robot with a 4K 3D Exoscope: The Future of Microsurgery
- PMID: 36983847
- PMCID: PMC10057826
- DOI: 10.3390/life13030692
First-in-Human Integrated Use of a Dedicated Microsurgical Robot with a 4K 3D Exoscope: The Future of Microsurgery
Abstract
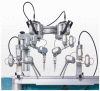
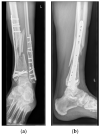
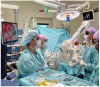
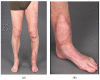
Innovative techniques can help overcome the limitations of the human body. Operating on very small structures requires adequate vision of the surgical field and precise movements of sophisticated instruments. Both the human eye and hand are limited when performing microsurgery. Conventional microsurgery uses operation microscopes to enhance the visualization of very small structures. Evolving technology of high-definition 3D cameras provides the opportunity to replace conventional operation microscopes, thereby improving ergonomics for surgeons. This leaves the human hand as a limiting factor in microsurgery. A dedicated robot for microsurgery has been developed to overcome this limitation and enhance the precision and stability of the surgeons' hands. We present the first-in-human case in reconstructive microsurgery where both technologies are integrated using a dedicated microsurgical robot in combination with a 4K 3D exoscope.
Keywords: exoscope; innovation; microsurgery; microsurgical robot; plastic and reconstructive surgery.
Conflict of interest statement
T.J.M.v.M. is medical advisor of Microsure, R.R.W.J.v.d.H. and T.J.M.v.M. are shareholders in Microsure.
Figures


References
-
- van Mulken T.J.M., Boymans C.A.E.M., Schols R.M., Cau R., Schoenmakers F.B.F., Hoekstra L.T., Qiu S.S., Selber J.C., Van Der Hulst R.R.W.J. Preclinical Experience Using a New Robotic System Created for Microsurgery. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2018;142:1367–1376. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000004939. - DOI - PubMed
-
- ORBEYE—4K 3D Orbital Camera System. Evolution in NeuroSurgery Imaging. [(accessed on 22 January 2023)]. Available online: https://www.olympus-europa.com/medical/en/Products-and-Solutions/Product....
-
- van Mulken T.J.M., Schols R.M., Qiu S.S., Brouwers K., Hoekstra L.T., Booi D.I., Cau R., Schoenmakers F., Scharmga A.M.J., Hulst R.R.W.J. Robotic (super) microsurgery: Feasibility of a new master-slave platform in an in vivo animal model and future directions. J. Surg. Oncol. 2018;118:826–831. doi: 10.1002/jso.25195. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

