Investigating the Efficiency of a Heat Recovery-Storage System Using Heat Pipes and Phase Change Materials
- PMID: 36984262
- PMCID: PMC10053556
- DOI: 10.3390/ma16062382
Investigating the Efficiency of a Heat Recovery-Storage System Using Heat Pipes and Phase Change Materials
Abstract
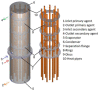
This study presents an experimental and numerical investigation into the efficiency of a two-stage heat recovery-storage system for reducing the thermal energy losses in the industry. The system is designed to recover and store waste thermal energy from residual fluids using heat pipes for recovery and an environmentally friendly phase change material for heat storage. Experimental investigation was conducted using water as the primary agent and varying the temperature between 60 °C, 65 °C, and 70 °C at a constant flow rate of 24 L/min. The secondary agent, also water, was used at an initial temperature of 10 °C and the flow rate was varied between 1 L/min, 2 L/min, and 3 L/min. The results show that the system had a peak efficiency of 78.1% and was able to recover a significant amount of thermal energy. This study demonstrates the potential of this system to reduce the thermal energy losses in the industry and highlight the importance of further research and development in this field, as the industry is responsible for approximately 14% of the total thermal energy losses and finding efficient ways to recover and store waste thermal energy is crucial to achieving sustainable energy consumption.
Keywords: PCM; heat pipe; heat recovery; heat storage.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures












References
-
- IEA (International Energy Agency) Perspectives on the Energy Transition. IEA; Paris, France: 2017.
-
- Jouhara H., Khordehgah N., Almahmoud S., Delpech B. Waste heat recovery technologies and applications. Therm. Sci. Eng. Prog. 2018;6:268–289. doi: 10.1016/j.tsep.2018.04.017. - DOI
-
- Jouhara H., Almahmoud S., Chauhan A., Delpech B., Bianchi G., Tassou S., Llera R., Lago F., Arribas J.J. Experimental and theoretical investigation of a flat heat pipe heat exchanger for waste heat recovery in the steel industry. Energy. 2017;141:1928–1939. doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2017.10.142. - DOI
-
- Delpech B., Axcell B., Jouhara H. Experimental investigation of a radiative heat pipe for waste heat recovery in a ceramics kiln. Energy. 2019;170:636–651. doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2018.12.133. - DOI
-
- Tian E., He Y.-L., Tao W.-Q. Research on a new type waste heat recovery gravity heat pipe exchanger. Appl. Energy. 2017;188:586–594. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2016.12.029. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

