Studies of Electrical Parameters and Thermal Stability of HiPIMS Hafnium Oxynitride (HfOxNy) Thin Films
- PMID: 36984417
- PMCID: PMC10051222
- DOI: 10.3390/ma16062539
Studies of Electrical Parameters and Thermal Stability of HiPIMS Hafnium Oxynitride (HfOxNy) Thin Films
Abstract
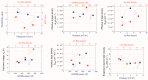
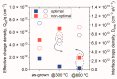
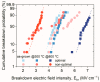
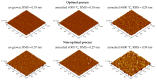
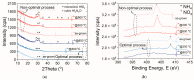
This work demonstrated the optimization of HiPIMS reactive magnetron sputtering of hafnium oxynitride (HfOxNy) thin films. During the optimization procedure, employing Taguchi orthogonal tables, the parameters of examined dielectric films were explored, utilizing optical methods (spectroscopic ellipsometry and refractometry), electrical characterization (C-V, I-V measurements of MOS structures), and structural investigation (AFM, XRD, XPS). The thermal stability of fabricated HfOxNy layers, up to 800 °C, was also investigated. The presented results demonstrated the correctness of the optimization methodology. The results also demonstrated the significant stability of hafnia-based layers at up to 800 °C. No electrical parameters or surface morphology deteriorations were demonstrated. The structural analysis revealed comparable electrical properties and significantly greater immunity to high-temperature treatment in HfOxNy layers formed using HiPIMS, as compared to those formed using the standard pulsed magnetron sputtering technique. The results presented in this study confirmed that the investigated hafnium oxynitride films, fabricated through the HiPIMS process, could potentially be used as a thermally-stable gate dielectric in self-aligned MOS structures and devices.
Keywords: HfOxNy; HiPIMS; MOS; electrical parameters; reactive magnetron sputtering; structural characterization; thermal stability.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures




References
-
- Wong H., Iwai H. On the scaling issues and high-k replacement of ultrathin gate dielectrics for nanoscale MOS transistors. Microelectron. Eng. 2006;83:1867–1904. doi: 10.1016/j.mee.2006.01.271. - DOI
-
- Koike M., Ino T., Koyama M., Kamata Y., Kamimuta Y., Suzuki M., Takashima A., Mitani Y., Nishiyama A., Tsunashima Y. Ultra-thin (EOT < 1:0nm) amorphous HfSiON gate insulator with high Hf concentration for high-performance logic applications; Proceedings of the 2003 International Conference on Solid State Devices and Materials; Tokyo, Japan. 16–18 September 2003; pp. 52–53.
-
- Driad R., Schmidt R., Kirste L., Loesch R., Mikulla M., Ambacher O. Hafnium oxide passivation of InGaAs/InP heterostructure bipolar transistors by electronbeam evaporation. Phys. Status Solidi. 2012;C9:381–384. doi: 10.1002/pssc.201100228. - DOI
-
- Khoshman J.M., Khan A., Kordesch M.E. Amorphous hafnium oxide thin films for antireflection optical coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2008;202:2500–2502. doi: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2007.07.095. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

