Atopic Dermatitis and Ulcerative Colitis Successfully Treated with Upadacitinib
- PMID: 36984542
- PMCID: PMC10058499
- DOI: 10.3390/medicina59030542
Atopic Dermatitis and Ulcerative Colitis Successfully Treated with Upadacitinib
Abstract
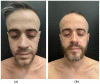
Background and Objectives: JAK inhibitors entered current clinical practice as treatment for several immune-related diseases and, recently, for atopic dermatitis. These drugs target the Janus Kinase intracellular cascade, rendering them suitable for treating both Th1 and Th2 immune-mediated responses. Materials and Methods: We report the case of a 36-year-old male patient presenting an overlap of ulcerative colitis, a Th1-related disease, and atopic dermatitis, a Th2-mediated condition. Treatment with upadacitinib was initiated, and laboratory and instrumental follow-ups were carried out for 8 months. Results: The complete and persistent clinical remission of both conditions was observed at a low dose of 15 mg of upadacitinib, even though ulcerative colitis guidelines usually recommend a dosage of 45 mg. No serious adverse responses to therapy were reported. Conclusions: Upadacitinib may be the most suitable management strategy in subjects with coexisting severe conditions mediated by Th1 inflammation, such as ulcerative colitis, and by Th2 cytokines, such as atopic dermatitis.
Keywords: Janus kinase; atopic dermatitis; patient selection; ulcerative colitis; upadacitinib.
Conflict of interest statement
T.G. has been an investigator for Abiogen, Eli Lilly and Co., and Sanofi, and has performed consultancies for Abbvie, Eli Lilly and Co., Laboratories Pierre Fabre, Novartis, and Sanofi. A.S. has performed consultancies for Sanofi and has received support for attending meetings by Eli Lilly and Co., Sanofi, and FIRMA. The other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Napolitano M., D’Amico F., Ragaini E., Peyrin-Biroulet L., Danese S. Evaluating Upadacitinib in the Treatment of Moderate-to-Severe Active Ulcerative Colitis: Design, Development, and Potential Position in Therapy. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2022;16:1897–1913. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S340459. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wollenberg A., Barbarot S., Bieber T., Christen-Zaech S., Deleuran M., Fink-Wagner A., Gieler U., Girolomoni G., Lau S., Muraro A., et al. Consensus-based European guidelines for treatment of atopic eczema (atopic dermatitis) in adults and children: Part I. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2018;32:657–682. doi: 10.1111/jdv.14891. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

