Pre-Test Probability Assessment and d-Dimer Based Evaluation in Patients with Previous Acute Aortic Syndrome
- PMID: 36984549
- PMCID: PMC10057941
- DOI: 10.3390/medicina59030548
Pre-Test Probability Assessment and d-Dimer Based Evaluation in Patients with Previous Acute Aortic Syndrome
Abstract
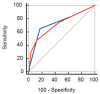
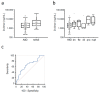
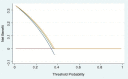
Background and Objectives. Acute aortic syndromes (AASs) are emergencies burdened by high morbidity and mortality. Guideline-recommended diagnostic workup is based on pre-test probability assessment (PPA) and d-dimer testing. However, the performance of PPA and d-dimer has never been studied in individuals with previous AAS (pAAS), which represent a challenging population. Materials and Methods. We analyzed a registry of patients with pAAS evaluated in two Emergency Departments (EDs) for suspected novel AAS (nAAS). Enrolment criteria were history of pAAS and the presence of truncal pain, syncope or perfusion deficit. All patients underwent advanced imaging. Clinical data were registered prospectively and PPA was performed by applying the aortic dissection detection (ADD) and an aorta simplified (AORTAs) score. Results. A total of 128 patients were enrolled, including 77 patients with previous Stanford type A aortic dissection and 45 patients with previous Stanford type B aortic dissection. The final diagnosis was nAAS in 40 (31%) patients. Clinical variables associated with nAAS were: aortic valve disease, thoracic aortic aneurysm, severe pain, sudden pain, ripping/tearing pain and hypotension/shock. ADD score ≥ 2 had a sensitivity of 65% and a specificity of 83% for nAAS; AORTAs score ≥ 2 had a sensitivity of 48% and a specificity of 88%. d-dimer (cutoff ≥ 500 ng/mL or age-adjusted cutoff) had a sensitivity of 97% and a specificity of 13%/14.7%, for diagnosis of nAAS. Patients that were candidates for guideline-compliant PPA/d-dimer integrated rule-out were: 5 (4.9%) with ADD ≤ 1/d-dimer and 8 (7.8%) with AORTAs ≤ 1/d-dimer < age-adjusted cutoff. None of them had a nAAS. Conclusions. Patients with pAAS evaluated in the ED for red-flag symptoms showed intermediate-to-high pre-test probability of nAAS. The ADD score had lower sensitivity and specificity than in unselected patients. d-dimer, alone and integrated with PPA, was highly sensitive for nAAS, but very unspecific. PPA/d-dimer integrated strategies are unlikely to significantly reduce the number of patients with pAAS undergoing advanced imaging.
Keywords: acute aortic syndrome; aortic dissection; clinical score; d-dimer; diagnosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; and in the decision to publish the results.
Figures