Circular Economy Approach in Treatment of Galvanic Wastewater Employing Membrane Processes
- PMID: 36984712
- PMCID: PMC10051783
- DOI: 10.3390/membranes13030325
Circular Economy Approach in Treatment of Galvanic Wastewater Employing Membrane Processes
Abstract
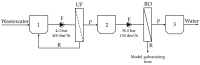
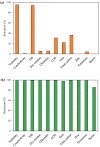
According to the idea of sustainable development, humanity should make every effort to care for the natural environment along with economic development. Decreasing water resources in the world makes it necessary to take action to reduce the consumption of this resource. This article presents the results of research conducted to improve the use of recyclable materials in line with the circular economy model. The research focused on the development of a technological solution for the recovery of raw materials from galvanic wastewater. The concept of a galvanic wastewater treatment system presented in the article includes wastewater pre-treatment in the ultrafiltration (UF) process and water recovery in the reverse osmosis (RO) process. In addition, the purpose of the work was to manage post-filtration waste (RO retentate) containing high concentrations of zinc in the process of galvanizing metal details. The obtained results indicate that it is possible to reduce the amount of sewage from the galvanizing industry by reusing the recovered water as technical water in the process line. The carried-out model tests of galvanizing confirmed the possibility of using RO retentate for the production of metal parts. The achieved results are a proposal to solve the problem of reducing the impact of galvanic wastewater on the environment and to improve the profitability of existing galvanizing technologies by reducing the consumption of water and raw materials.
Keywords: circular economy; galvanic wastewater; reverse osmosis (RO); ultrafiltration (UF); water recovery; zinc solution reuse.
Conflict of interest statement
This manuscript’s authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Velazquez-Peña S., Barrera-Díaz C., Linares-Hernández I., Bilyeu B., Martínez-Delgadillo S.A. An effective electrochemical Cr(VI) removal contained in electroplating industry wastewater and the chemical characterization of the sludge produced. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012;51:5905–5910. doi: 10.1021/ie200968s. - DOI
-
- Yaqoob A.A., Guerrero–Barajas C., Ahmad A., Ibrahim M.N.M., Alshammari M.B. Green Chemistry for Sustainable Water Purification. John Wiley & Sons, Inc.; New York, NY, USA: 2023. Advanced Technologies for Wastewater Treatment; pp. 179–202.
-
- Zelinski R., Silvestre W.P., Duarte J., Livinalli N.F., Zeni M., Baldasso C. Evaluation of the use of reverse osmosis in the treatment of galvanic effluents. J. Membr. Sci. Res. 2023;9:562616.
-
- Chavez Porras Á., Cristancho Montenegro D.L., Ospina Granados É.A. A clean alternative for galvanic wastewater treatment: Literature review. Rev. Ing. Univ. Medellin. 2009;8:39–50.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

