Incorporation of Plant-Based Diet Surpasses Current Standards in Therapeutic Outcomes in Inflammatory Bowel Disease
- PMID: 36984772
- PMCID: PMC10051661
- DOI: 10.3390/metabo13030332
Incorporation of Plant-Based Diet Surpasses Current Standards in Therapeutic Outcomes in Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Abstract
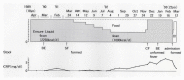
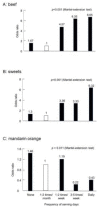
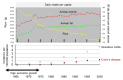
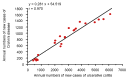
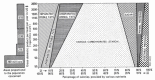
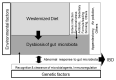
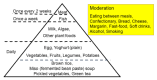
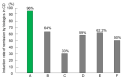
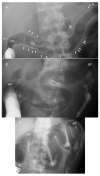
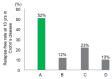
There has been no study of the therapeutic effect of a plant-based diet (PBD) in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) except for our studies in Japan. In this review, we describe the rationale for the requirement of PBD in IBD and the outcomes of our modality incorporating PBD together with a literature review. The biggest problem in current therapy for IBD is the lack of a widely appreciated ubiquitous environmental factor in IBD. Therefore, a radical strategy against IBD has not been established. Japanese data showed an increased incidence of IBD in association with dietary westernization. Current global consumption consists of an excess of unhealthy foods and a shortage of healthy foods recognized as pro-inflammatory. Patients with IBD are no exception. One of the recommended healthy reference diets is PBD recognized as anti-inflammatory. We assert that IBD occurs in susceptible individuals mainly as a result of our omnivorous (westernized) diet. Therefore, we developed and began to provide a PBD, a lacto-ovo-vegetarian diet, for IBD patients in 2003. Infliximab and PBD as first-line (IPF) therapy was administered for all patients with newly developed Crohn's disease (CD) and for severe ulcerative colitis (UC). Our modality broke the barrier of primary nonresponders to biologics, with a remission rate of 96% in CD, and created a new relapse-free course in slightly over half of the patients (52%) with CD. Based on the rationale derived from available evidence and the clinical outcomes, PBD is highly recommended for IBD.
Keywords: Crohn’s disease; diet; inflammatory bowel disease; natural course; plant-based diet; relapse; semi-vegetarian diet; therapy; ulcerative colitis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




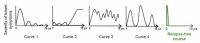
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

