GABA Metabolism, Transport and Their Roles and Mechanisms in the Regulation of Abiotic Stress (Hypoxia, Salt, Drought) Resistance in Plants
- PMID: 36984787
- PMCID: PMC10051757
- DOI: 10.3390/metabo13030347
GABA Metabolism, Transport and Their Roles and Mechanisms in the Regulation of Abiotic Stress (Hypoxia, Salt, Drought) Resistance in Plants
Abstract
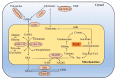
γ- Aminobutyric acid (GABA) is a ubiquitous four-carbon non-protein amino acid. In plants, GABA is found in different cell compartments and performs different metabolic functions. As a signalling molecule, GABA participates in the regulation of tolerance to various abiotic stresses. Many research studies have found that GABA accumulates in large amounts when plants are subjected to abiotic stress, which have been demonstrated through the Web of Science, PubMed, Elsevier and other databases. GABA enhances the tolerance of plants to abiotic stress by regulating intracellular pH, ion transport, activating antioxidant systems and scavenging active oxygen species. In the process of GABA playing its role, transport is very important for the accumulation and metabolism pathway of GABA in cells. Therefore, the research on the transport of GABA across the cell membrane and the organelle membrane by transport proteins is a direction worthy of attention. This paper describes the distribution, biosynthesis and catabolism of GABA in plants. In addition, we focus on the latest progress in research on the transport of exogenous GABA and on the function and mechanism in the regulation of the abiotic stress response. Based on this summary of the role of GABA in the resistance to various abiotic stresses, we conclude that GABA has become an effective compound for improving plant abiotic tolerance.
Keywords: biosynthesis and catabolism; distribution; plant growth and development; transporter from intracellular and extracellular; γ- aminobutyric acid.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
"Deciphering the enigmatic role of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) in plants: Synthesis, transport, regulation, signaling, and biological roles in interaction with growth regulators and abiotic stresses.".Plant Physiol Biochem. 2024 Mar;208:108502. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2024.108502. Epub 2024 Mar 8. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2024. PMID: 38492486 Review.
-
Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) alleviates salt damage in tomato by modulating Na+ uptake, the GAD gene, amino acid synthesis and reactive oxygen species metabolism.BMC Plant Biol. 2020 Oct 9;20(1):465. doi: 10.1186/s12870-020-02669-w. BMC Plant Biol. 2020. PMID: 33036565 Free PMC article.
-
The versatile GABA in plants.Plant Signal Behav. 2021 Mar 4;16(3):1862565. doi: 10.1080/15592324.2020.1862565. Epub 2021 Jan 6. Plant Signal Behav. 2021. PMID: 33404284 Free PMC article. Review.
-
iTRAQ-based proteomics reveals key role of γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) in regulating drought tolerance in perennial creeping bentgrass (Agrostis stolonifera).Plant Physiol Biochem. 2019 Dec;145:216-226. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2019.10.018. Epub 2019 Nov 1. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2019. PMID: 31707249
-
Virus-induced gene silencing reveals control of reactive oxygen species accumulation and salt tolerance in tomato by γ-aminobutyric acid metabolic pathway.Plant Cell Environ. 2015 Mar;38(3):600-13. doi: 10.1111/pce.12419. Epub 2014 Aug 27. Plant Cell Environ. 2015. PMID: 25074245
Cited by
-
Pilot investigation of the rhizosphere microbial communities and metabolism of two cultivars of Polygonatum cyrtonema Hua.Front Microbiol. 2025 Jul 23;16:1615900. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1615900. eCollection 2025. Front Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40771688 Free PMC article.
-
Silicon nanoparticles (SiNPs) mediate GABA, SOD and ASA-GSH cycle to improve cd stress tolerance in Solanum lycopersicum.Sci Rep. 2024 Sep 20;14(1):21948. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-72908-9. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39304700 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancement of γ-Aminobutyric Acid and the Characteristics of Nutrition and Function in White Quinoa through Ultrasound Stress at the Pre-Germination Stage.Foods. 2023 Dec 22;13(1):57. doi: 10.3390/foods13010057. Foods. 2023. PMID: 38201084 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Evaluation of Chemical Composition and Nutritional Characteristics in Various Quinoa Sprout Varieties: The Superiority of 24-Hour Germination.Foods. 2024 Aug 12;13(16):2513. doi: 10.3390/foods13162513. Foods. 2024. PMID: 39200439 Free PMC article.
-
Integrating transcriptome and metabolome to explore the growth-promoting mechanisms of GABA in blueberry plantlets.Front Plant Sci. 2023 Dec 21;14:1319700. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1319700. eCollection 2023. Front Plant Sci. 2023. PMID: 38186593 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Steward F.C., Thompson J.F., Dent C.E. γ-Aminobutyric acid: A constituent of the potato tuber? Science. 1949;110:439–440.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials