Biopreservative Effect of the Tunisian Halophyte Lobularia maritima Flavonoid Fraction, Used Alone and in Combination with Linalool in Stored Minced Beef Meat
- PMID: 36984811
- PMCID: PMC10057118
- DOI: 10.3390/metabo13030371
Biopreservative Effect of the Tunisian Halophyte Lobularia maritima Flavonoid Fraction, Used Alone and in Combination with Linalool in Stored Minced Beef Meat
Abstract
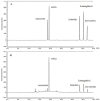
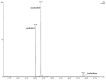
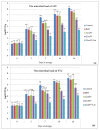
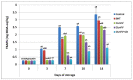
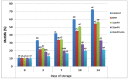
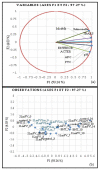
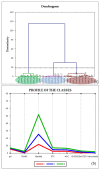
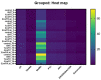
In the present study, Lobularia maritima (Lm) flavonoid extract (LmFV) was characterized by HPLC analyses and five compounds were detected. Further, to describe the chemical content of the matrix, GC-MS analyses after silylation were performed; the obtained results showed the presence of a large number of components belonging to several chemical classes, mostly sugar alcohols, sugars, fatty acids, and terpenes. Firstly, the antibacterial activities of this fraction and linalool (Lin) were evaluated against eight foodborne pathogenic strains with MIC values between 2.3 and 5.8 mg/mL and 0.23 and 0.7 mg/mL, respectively. Then, the antioxidant activity of both was evaluated by the DPPH antiradical test and the phosphomolybdenum test. Furthermore, the biopreservative effect of LmFV alone and in combination with Lin on minced beef stored at 4 °C for 14 days was evaluated using microbiological and physiochemical tests. LmFV at 4.6% alone significantly reduced microbial spoilage in ground meat (p < 0.05). The combination of LmFV (4.6%) and Lin (0.46%) was more effective than LmFV alone in inhibiting bacterial contamination, reducing TBARS values and the risk of bacterial contamination, and reducing the accumulation of Met myoglobin (MetMb). This combination, therefore, extends the shelf life of the product by about 10 days. Based on these microbiological results and physicochemical parameters, it can be stated that the addition of Lin potentiates the flavonoid fraction of L. maritima more strongly against the deterioration of meat quality by significantly improving its biopreservative effect as a natural conservative.
Keywords: antioxidant activity; chemical composition; flavonoid extract; linalool; microbial spoilage; minced beef meat; multivariate analysis; synergistic effect.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Essential Oil of Tunisian Halophyte Lobularia maritima: A Natural Food Preservative Agent of Ground Beef Meat.Life (Basel). 2022 Oct 10;12(10):1571. doi: 10.3390/life12101571. Life (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36295006 Free PMC article.
-
Stress associated protein from Lobularia maritima: Heterologous expression, antioxidant and antimicrobial activities with its preservative effect against Listeria monocytogenes inoculated in beef meat.Int J Biol Macromol. 2019 Jul 1;132:888-896. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.04.012. Epub 2019 Apr 3. Int J Biol Macromol. 2019. PMID: 30953725
-
A New Approach in Meat Bio-Preservation through the Incorporation of a Heteropolysaccharide Isolated from Lobularia maritima L.Foods. 2022 Dec 6;11(23):3935. doi: 10.3390/foods11233935. Foods. 2022. PMID: 36496743 Free PMC article.
-
Bio-preservative effect of the essential oil of the endemic Mentha piperita used alone and in combination with BacTN635 in stored minced beef meat.Meat Sci. 2016 Jul;117:196-204. doi: 10.1016/j.meatsci.2016.03.006. Epub 2016 Mar 10. Meat Sci. 2016. PMID: 26995774
-
Synergistic Effect of Combination of Various Microbial Hurdles in the Biopreservation of Meat and Meat Products-Systematic Review.Foods. 2023 Mar 28;12(7):1430. doi: 10.3390/foods12071430. Foods. 2023. PMID: 37048251 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Insight into Pelargonium odoratissimum Essential Oil Preservative Properties Effect on Ground Beef.Foods. 2024 Oct 7;13(19):3181. doi: 10.3390/foods13193181. Foods. 2024. PMID: 39410216 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated lipidomics and microbiomics reveal the quality changes of fresh yak tenderloin during storage.Food Chem X. 2024 Nov 8;24:101984. doi: 10.1016/j.fochx.2024.101984. eCollection 2024 Dec 30. Food Chem X. 2024. PMID: 39629284 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances in the Incorporation of Polysaccharides with Antioxidant and Antibacterial Functions to Preserve the Quality and Shelf Life of Meat Products.Foods. 2023 Apr 14;12(8):1647. doi: 10.3390/foods12081647. Foods. 2023. PMID: 37107442 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Study of the Chemical Composition and Biological Activity of Michelia macclurei Dandy Heartwood: New Sources of Natural Antioxidants, Enzyme Inhibitors and Bacterial Inhibitors.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 28;24(9):7972. doi: 10.3390/ijms24097972. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37175683 Free PMC article.
-
Secondary Metabolites and Biological Activities From Achillea gypsicola Hub-Mor. Under Foliar Applications of Chitosan and Salicylic Acid.Food Sci Nutr. 2025 May 12;13(5):e70225. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.70225. eCollection 2025 May. Food Sci Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40357338 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Addi M., Elbouzidi A., Abid M., Tungmunnithum D., Elamrani A., Hano C. An Overview of Bioactive Flavonoids from Citrus Fruits. Appl. Sci. 2022;12:29. doi: 10.3390/app12010029. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

