Biosynthesis of Phytocannabinoids and Structural Insights: A Review
- PMID: 36984882
- PMCID: PMC10051821
- DOI: 10.3390/metabo13030442
Biosynthesis of Phytocannabinoids and Structural Insights: A Review
Abstract
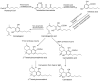
Cannabis belongs to the family Cannabaceae, and phytocannabinoids are produced by the Cannabis sativa L. plant. A long-standing debate regarding the plant is whether it contains one or more species. Phytocannabinoids are bioactive natural products found in flowers, seeds, and fruits. They can be beneficial for treating human diseases (such as multiple sclerosis, neurodegenerative diseases, epilepsy, and pain), the cellular metabolic process, and regulating biological function systems. In addition, several phytocannabinoids are used in various therapeutic and pharmaceutical applications. This study provides an overview of the different sources of phytocannabinoids; further, the biosynthesis of bioactive compounds involving various pathways is elucidated. The structural classification of phytocannabinoids is based on their decorated resorcinol core and the bioactivities of naturally occurring cannabinoids. Furthermore, phytocannabinoids have been studied in terms of their role in animal models and antimicrobial activity against bacteria and fungi; further, they show potential for therapeutic applications and are used in treating various human diseases. Overall, this review can help deepen the current understanding of the role of biotechnological approaches and the importance of phytocannabinoids in different industrial applications.
Keywords: Cannabis sativa L.; biosynthesis pathways; industrial application; phytocannabinoids; structural activity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Schultes R.E., Klein W.M., Plowman T., Lockwood T.E. Cannabis: An example of taxonomic neglect. Bot. Mus. Lealf. Harv. Univ. 1974;23:337–367. doi: 10.5962/p.168565. - DOI
-
- Chen C., Pan Z. Cannabidiol and terpenes from hemp–ingredients for future foods and processing technologies. J. Futur. Foods. 2021;1:113–127. doi: 10.1016/j.jfutfo.2022.01.001. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

