TEER and Ion Selective Transwell-Integrated Sensors System for Caco-2 Cell Model
- PMID: 36984903
- PMCID: PMC10054836
- DOI: 10.3390/mi14030496
TEER and Ion Selective Transwell-Integrated Sensors System for Caco-2 Cell Model
Abstract
Monitoring of ions in real-time directly in cell culture systems and in organ-on-a-chip platforms represents a significant investigation tool to understand ion regulation and distribution in the body and ions' involvement in biological mechanisms and specific pathologies. Innovative flexible sensors coupling electrochemical stripping analysis (square wave anodic stripping voltammetry, SWASV) with an ion selective membrane (ISM) were developed and integrated in Transwell™ cell culture systems to investigate the transport of zinc and copper ions across a human intestinal Caco-2 cell monolayer. The fabricated ion-selective sensors demonstrated good sensitivity (1 × 10-11 M ion concentration) and low detection limits, consistent with pathophysiological cellular concentration ranges. A non-invasive electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) analysis, in situ, across a selected spectrum of frequencies (10-105 Hz), and an equivalent circuit fitting were employed to obtain useful electrical parameters for cellular barrier integrity monitoring. Transepithelial electrical resistance (TEER) data and immunofluorescent images were used to validate the intestinal epithelial integrity and the permeability enhancer effect of ethylene glycol-bis(2-aminoethylether)-N,N,N',N'-tetraacetic acid (EGTA) treatment. The proposed devices represent a real prospective tool for monitoring cellular and molecular events and for studies on gut metabolism/permeability. They will enable a rapid integration of these sensors into gut-on-chip systems.
Keywords: Caco-2 monolayer; Transwell™ plate; anodic stripping voltammetry; electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS); organ-on-a-chip (OoC); transepithelial electrical resistance (TEER).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


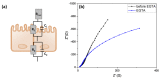
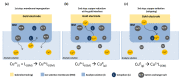

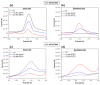
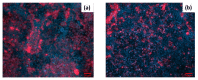
References
-
- Kassanos P., Seichepine F., Wales D., Yang G.-Z. Towards a Flexible/Stretchable Multiparametric Sensing Device for Surgical and Wearable Applications; Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Biomedical Circuits and Systems Conference (BioCAS); Nara, Japan. 17–19 October 2019;
-
- Chmayssem A., Verplanck N., Tanase C.E., Costa G., Monsalve-Grijalba K., Amigues S., Alias M., Gougis M., Mourier V., Vignoud S., et al. Development of a Multiparametric (Bio)Sensing Platform for Continuous Monitoring of Stress Metabolites. Talanta. 2021;229:122275. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2021.122275. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ding J., Qin W. Recent Advances in Potentiometric Biosensors. TrAC—Trends Anal. Chem. 2020;124:115803. doi: 10.1016/j.trac.2019.115803. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

