Iron-Vanadium Incorporated Ferrocyanides as Potential Cathode Materials for Application in Sodium-Ion Batteries
- PMID: 36984928
- PMCID: PMC10059089
- DOI: 10.3390/mi14030521
Iron-Vanadium Incorporated Ferrocyanides as Potential Cathode Materials for Application in Sodium-Ion Batteries
Abstract
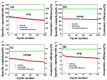
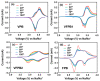
Sodium-ion batteries (SIBs) are potential replacements for lithium-ion batteries owing to their comparable energy density and the abundance of sodium. However, the low potential and low stability of their cathode materials have prevented their commercialization. Prussian blue analogs are ideal cathode materials for SIBs owing to the numerous diffusion channels in their 3D structure and their high potential vs. Na/Na+. In this study, we fabricated various Fe-V-incorporated hexacyanoferrates, which are Prussian blue analogs, via a one-step synthesis. These compounds changed their colors from blue to green to yellow with increasing amounts of incorporated V ions. The X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy spectrum revealed that V3+ was oxidized to V4+ in the cubic Prussian blue structure, which enhanced the electrochemical stability and increased the voltage platform. The vanadium ferrocyanide Prussian blue (VFPB1) electrode, which contains V4+ and Fe2+ in the Prussian blue structure, showed Na insertion/extraction potential of 3.26/3.65 V vs. Na/Na+. The cycling test revealed a stable capacity of ~70 mAh g-1 at a rate of 50 mA g-1 and a capacity retention of 82.5% after 100 cycles. We believe that this Fe-V-incorporated Prussian green cathode material is a promising candidate for stable and high-voltage cathodes for SIBs.
Keywords: Prussian blue; Prussian green; high-voltage cathode; sodium-ion batteries; vanadium.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Recent Advances in Sodium-Ion Batteries: Cathode Materials.Materials (Basel). 2023 Oct 26;16(21):6869. doi: 10.3390/ma16216869. Materials (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37959466 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vanadium Ferrocyanides as a Highly Stable Cathode for Lithium-Ion Batteries.Molecules. 2023 Jan 4;28(2):461. doi: 10.3390/molecules28020461. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 36677524 Free PMC article.
-
A Chemical Precipitation Method Preparing Hollow-Core-Shell Heterostructures Based on the Prussian Blue Analogs as Cathode for Sodium-Ion Batteries.Small. 2018 Jul;14(28):e1801246. doi: 10.1002/smll.201801246. Epub 2018 Jun 7. Small. 2018. PMID: 29882323
-
Preparation of Prussian Blue Submicron Particles with a Pore Structure by Two-Step Optimization for Na-Ion Battery Cathodes.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016 Jun 29;8(25):16078-86. doi: 10.1021/acsami.6b04151. Epub 2016 Jun 14. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016. PMID: 27267656
-
Research Progress of Prussian Blue and Its Analogs as High-Performance Cathode Nanomaterials for Sodium-Ion Batteries.Small Methods. 2024 Aug;8(8):e2301372. doi: 10.1002/smtd.202301372. Epub 2023 Dec 14. Small Methods. 2024. PMID: 38098164 Review.
Cited by
-
Recent Advances in Sodium-Ion Batteries: Cathode Materials.Materials (Basel). 2023 Oct 26;16(21):6869. doi: 10.3390/ma16216869. Materials (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37959466 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Asenbauer J., Eisenmann T., Kuenzel M., Kazzazi A., Chen Z., Bresser D. The success story of graphite as a lithium-ion anode material-fundamentals, remaining challenges, and recent developments including silicon (oxide) composites. Sustain. Energy Fuels. 2020;4:5387–5416. doi: 10.1039/D0SE00175A. - DOI
-
- Assawaworrarit S., Omair Z., Fan S. Nighttime electric power generation at a density of 50 mW/m2 via radiative cooling of a photovoltaic cell. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2022;120:143901. doi: 10.1063/5.0085205. - DOI
-
- Goodenough J.B., Kim Y. Challenges for Rechargeable Li Batteries. Chem. Mater. 2010;22:587–603. doi: 10.1021/cm901452z. - DOI
-
- Nguyen T.P., Giang T.T., Kim I.T. Restructuring NiO to LiNiO2: Ultrastable and reversible anodes for lithium-ion batteries. Chem. Eng. J. 2022;437:135292. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2022.135292. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

