Viscoelastic Particle Encapsulation Using a Hyaluronic Acid Solution in a T-Junction Microfluidic Device
- PMID: 36984969
- PMCID: PMC10053877
- DOI: 10.3390/mi14030563
Viscoelastic Particle Encapsulation Using a Hyaluronic Acid Solution in a T-Junction Microfluidic Device
Abstract
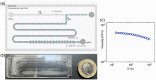
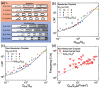
The encapsulation of particles and cells in droplets is highly relevant in biomedical engineering as well as in material science. So far, however, the majority of the studies in this area have focused on the encapsulation of particles or cells suspended in Newtonian liquids. We here studied the particle encapsulation phenomenon in a T-junction microfluidic device, using a non-Newtonian viscoelastic hyaluronic acid solution in phosphate buffer saline as suspending liquid for the particles. We first studied the non-Newtonian droplet formation mechanism, finding that the data for the normalised droplet length scaled as the Newtonian ones. We then performed viscoelastic encapsulation experiments, where we exploited the fact that particles self-assembled in equally-spaced structures before approaching the encapsulation area, to then identify some experimental conditions for which the single encapsulation efficiency was larger than the stochastic limit predicted by the Poisson statistics.
Keywords: droplet microfluidics; non-newtonian liquids; viscoelasticity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Liu Y., Fan Z., Qiao L., Liu B. Advances in microfluidic strategies for single-cell research. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2022;157:116822. doi: 10.1016/j.trac.2022.116822. - DOI
-
- Huang L., Chen Y., Zhou J. Interrogation of single-cell communications on microfluidic platforms. Cell Rep. Phys. Sci. 2022;3:101129. doi: 10.1016/j.xcrp.2022.101129. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

