Analysis of Von Kármán Swirling Flows Due to a Porous Rotating Disk Electrode
- PMID: 36984988
- PMCID: PMC10056891
- DOI: 10.3390/mi14030582
Analysis of Von Kármán Swirling Flows Due to a Porous Rotating Disk Electrode
Abstract
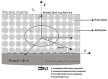
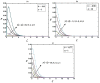
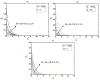
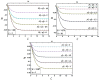
The study of Von Kármán swirling flow is a subject of active interest due to its applications in a wide range of fields, including biofuel manufacturing, rotating heat exchangers, rotating disc reactors, liquid metal pumping engines, food processing, electric power generating systems, designs of multi-pore distributors, and many others. This paper focusses on investigating Von Kármán swirling flows of viscous incompressible fluid due to a rotating disk electrode. The model is based on a system of four coupled second-order non-linear differential equations. The purpose of the present communication is to derive analytical expressions of velocity components by solving the non-linear equations using the homotopy analysis method. Combined effects of the slip λ and porosity γ parameters are studied in detail. If either parameter is increased, all velocity components are reduced, as both have the same effect on the mean velocity profiles. The porosity parameter γ increases the moment coefficient at the disk surface, which monotonically decreases with the slip parameter λ. The analytical results are also compared with numerical solutions, which are in satisfactory agreement. Furthermore, the effects of porosity and slip parameters on velocity profiles are discussed.
Keywords: homotopy analysis method; mathematical modeling; non-linear differential equations; rotating disk electrodes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Numerical Analysis of Thermal Radiative Maxwell Nanofluid Flow Over-Stretching Porous Rotating Disk.Micromachines (Basel). 2021 May 10;12(5):540. doi: 10.3390/mi12050540. Micromachines (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34068521 Free PMC article.
-
A numerical study of chemical reaction in a nanofluid flow due to rotating disk in the presence of magnetic field.Sci Rep. 2021 Sep 29;11(1):19399. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-98881-1. Sci Rep. 2021. Retraction in: Sci Rep. 2023 May 10;13(1):7605. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-34630-w. PMID: 34588553 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Scrutinization of second law analysis and viscous dissipation on Reiner-RivlinNanofluid with the effect of bioconvection over a rotating disk.Heliyon. 2023 Jan 20;9(2):e13091. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e13091. eCollection 2023 Feb. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 36798776 Free PMC article.
-
Carbon Nanotubes Flow Induced by Rotating Stretching Disk with Non- Linear Radiations and Slip.Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2022;25(14):2498-2508. doi: 10.2174/1386207324666210709095532. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2022. PMID: 34254907
-
Instability analysis for MHD boundary layer flow of nanofluid over a rotating disk with anisotropic and isotropic roughness.Heliyon. 2024 Mar 1;10(6):e26779. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e26779. eCollection 2024 Mar 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38509923 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kataoka H., Tomiyama A., Hosokawa S., Sou A., Chaki M. Two-phase swirling flow in a gas-liquid separator. J. Power Energy Sys. 2008;2:1120–1131. doi: 10.1299/jpes.2.1120. - DOI
-
- Bonnecaze R., Mano N., Nam B., Heller A. On the behavior of the porous rotating disc electrode. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2007;154:F44–F47. doi: 10.1149/1.2403082. - DOI
-
- Vargas R., Borrás C., Mostanya J., Scharifker B.R. Kinetics of surface reactions on rotating disk electrodes. Electrochim. Acta. 2012;80:326–333. doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2012.07.025. - DOI
-
- Miklavcic M.M., Wang C.Y. The Flow due to a Rough Rotating Disk. J. ApplMath. Phys. 2004;55:235–246. doi: 10.1007/s00033-003-2096-6. - DOI
-
- Turkyilmazoglu M., Senel P. Heat and mass transfer of the flow due to a rotating rough and porous disk. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2013;63:146–158. doi: 10.1016/j.ijthermalsci.2012.07.013. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

