Fecal Volatile Metabolomics Predict Gram-Negative Late-Onset Sepsis in Preterm Infants: A Nationwide Case-Control Study
- PMID: 36985146
- PMCID: PMC10054547
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms11030572
Fecal Volatile Metabolomics Predict Gram-Negative Late-Onset Sepsis in Preterm Infants: A Nationwide Case-Control Study
Abstract
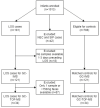
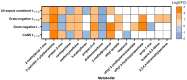
Early detection of late-onset sepsis (LOS) in preterm infants is crucial since timely treatment initiation is a key prognostic factor. We hypothesized that fecal volatile organic compounds (VOCs), reflecting microbiota composition and function, could serve as a non-invasive biomarker for preclinical pathogen-specific LOS detection. Fecal samples and clinical data of all preterm infants (≤30 weeks' gestation) admitted at nine neonatal intensive care units in the Netherlands and Belgium were collected daily. Samples from one to three days before LOS onset were analyzed by gas chromatography-ion mobility spectrometry (GC-IMS), a technique based on pattern recognition, and gas chromatography-time of flight-mass spectrometry (GC-TOF-MS), to identify unique metabolites. Fecal VOC profiles and metabolites from infants with LOS were compared with matched controls. Samples from 121 LOS infants and 121 matched controls were analyzed using GC-IMS, and from 34 LOS infants and 34 matched controls using GC-TOF-MS. Differences in fecal VOCs were most profound one and two days preceding Escherichia coli LOS (Area Under Curve; p-value: 0.73; p = 0.02, 0.83; p < 0.002, respectively) and two and three days before gram-negative LOS (0.81; p < 0.001, 0.85; p < 0.001, respectively). GC-TOF-MS identified pathogen-specific discriminative metabolites for LOS. This study underlines the potential for VOCs as a non-invasive preclinical diagnostic LOS biomarker.
Keywords: fecal biomarker; gas chromatography—ion mobility spectrometry; gas chromatography—time of flight—mass spectrometry; microbiota; neonatology; volatile organic compounds.
Conflict of interest statement
None of the co-authors received a honorarium, grant, or other form of payment for the production of this manuscript. Outside the submitted work, N.K.H.d.B. has served as a speaker for AbbVie and MSD. He has also served as a consultant and/or principal investigator for TEVA Pharma BV and Takeda. He has received a (unrestricted) research grant from Dr Falk, TEVA Pharma BV, MLDS and Takeda. The other authors have nothing to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Stoll B.J., Hansen N., Fanaroff A.A., Wright L.L., Carlo W.A., Ehrenkranz R.A., Lemons J.A., Donovan E.F., Stark A.R., Tyson J.E., et al. Late-Onset Sepsis in Very Low Birth Weight Neonates: The Experience of the NICHD Neonatal Research Network. Pediatrics. 2002;110:285–291. doi: 10.1542/peds.110.2.285. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

