Lactobacillus salivarius WZ1 Inhibits the Inflammatory Injury of Mouse Jejunum Caused by Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli K88 by Regulating the TLR4/NF-κB/MyD88 Inflammatory Pathway and Gut Microbiota
- PMID: 36985229
- PMCID: PMC10055675
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms11030657
Lactobacillus salivarius WZ1 Inhibits the Inflammatory Injury of Mouse Jejunum Caused by Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli K88 by Regulating the TLR4/NF-κB/MyD88 Inflammatory Pathway and Gut Microbiota
Abstract
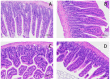
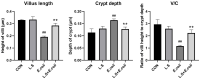
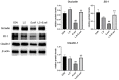
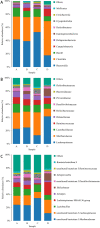
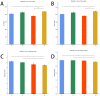
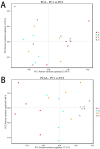
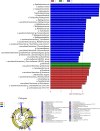
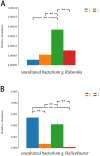
Replacing antibiotics with probiotics has become an important way to safely and effectively prevent and treat some gastrointestinal diseases. This study was conducted to investigate whether Lactobacillus salivarius WZ1 (L.S) could reduce the inflammatory injury to the mouse jejunum induced by Escherichia coli (ETEC) K88. Forty Kunming mice were randomly divided into four groups with 10 mice in each group. From day 1 to day 14, the control group and the E. coli group were administered with normal saline each day, while the L.S group and the L.S + E. coli group were gavaged with Lactobacillus salivarius WZ1 1 × 108 CFU/mL each day. On the 15th day, the E. coli group and the L.S + E. coli group were intragastrically administered ETEC K88 1 × 109 CFU/mL and sacrificed 24 h later. Our results show that pretreatment with Lactobacillus salivarius WZ1 can dramatically protect the jejunum morphological structure from the changes caused by ETEC K88 and relieve the morphological lesions of the jejunum, inhibiting changes in the mRNA expressions of TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-6 and the protein expressions of TLR4, NF-κB and MyD88 in the intestinal tissue of mice caused by ETEC K88. Moreover, pretreatment with Lactobacillus salivarius WZ1 also increased the relative abundance of beneficial genera such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium and decreased the abundance of harmful genera such as Ralstonia and Helicobacter in the gut. These results demonstrate that Lactobacillus salivarius WZ1 can inhibit the inflammatory damage caused by ETEC K88 in mouse jejunum by regulating the TLR4/NF-κB/MyD88 inflammatory pathway and gut microbiota.
Keywords: ETEC K88; Lactobacillus salivarius; TLR4/NF-κB/MyD88; gut microbiota; inflammatory injury; mice.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Prieto A., Lopez-Novo C., Diaz P., Diaz-Cao J.M., Lopez-Lorenzo G., Anton C., Remesar S., Garcia-Dios D., Lopez C., Panadero R., et al. Antimicrobial Susceptibility of Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli from Diarrhoeic Neonatal Calves in Spain. Animals. 2022;12:264. doi: 10.3390/ani12030264. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

