Probiotic Bifidobacterium breve MCC1274 Protects against Oxidative Stress and Neuronal Lipid Droplet Formation via PLIN4 Gene Regulation
- PMID: 36985364
- PMCID: PMC10052176
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms11030791
Probiotic Bifidobacterium breve MCC1274 Protects against Oxidative Stress and Neuronal Lipid Droplet Formation via PLIN4 Gene Regulation
Abstract
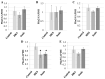
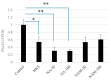
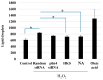
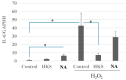
Consumption of Bifidobacterium breve MCC1274 has been shown to improve memory and prevent brain atrophy in populations with mild cognitive impairment (MCI). Preclinical in vivo studies using Alzheimer's disease (AD) models indicate that this probiotic protects against brain inflammation. There is growing evidence that lipid droplets are associated with brain inflammation, and lipid-associated proteins called perilipins could play an important role in neurodegenerative diseases such as dementia. In this study, we found that B. breve MCC1274 cell extracts significantly decreased the expression of perilipin 4 (PLIN4), which encodes a lipid droplet docking protein whose expression is known to be increased during inflammation in SH-SY5Y cells. Niacin, an MCC1274 cell extract component, increased PLIN4 expression by itself. Moreover, MCC1274 cell extracts and niacin blocked the PLIN4 induction caused by oxidative stress in SH-SY5Y cells, reduced lipid droplet formation, and prevented IL-6 cytokine production. These results offer a possible explanation for the effect of this strain on brain inflammation.
Keywords: Bifidobacterium breve; PLIN4; inflammation; lipid droplets; niacin; oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Protective Effects of Bifidobacterium Breve MCC1274 as a Novel Therapy for Alzheimer's Disease.Nutrients. 2025 Jan 31;17(3):558. doi: 10.3390/nu17030558. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 39940416 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potential Therapeutic Effects of Bifidobacterium breve MCC1274 on Alzheimer's Disease Pathologies in AppNL-G-F Mice.Nutrients. 2024 Feb 15;16(4):538. doi: 10.3390/nu16040538. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38398861 Free PMC article.
-
Probiotic Bifidobacterium breve MCC1274 Mitigates Alzheimer's Disease-Related Pathologies in Wild-Type Mice.Nutrients. 2022 Jun 19;14(12):2543. doi: 10.3390/nu14122543. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 35745273 Free PMC article.
-
Bifidobacterium breve MCC1274 Supplementation Increased the Plasma Levels of Metabolites with Potential Anti-Oxidative Activity in APP Knock-In Mice.J Alzheimers Dis. 2022;89(4):1413-1425. doi: 10.3233/JAD-220479. J Alzheimers Dis. 2022. PMID: 36057824 Free PMC article.
-
Beneficial Effects of Walnuts on Cognition and Brain Health.Nutrients. 2020 Feb 20;12(2):550. doi: 10.3390/nu12020550. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 32093220 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Protective Effects of Bifidobacterium Breve MCC1274 as a Novel Therapy for Alzheimer's Disease.Nutrients. 2025 Jan 31;17(3):558. doi: 10.3390/nu17030558. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 39940416 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Perilipins in Oxidative Stress-Implications for Cardiovascular Disease.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Feb 7;13(2):209. doi: 10.3390/antiox13020209. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38397807 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ATP11B Modulates Microglial Lipid Metabolism and Alleviates Alzheimer's Disease Pathology.MedComm (2020). 2025 Mar 22;6(4):e70139. doi: 10.1002/mco2.70139. eCollection 2025 Apr. MedComm (2020). 2025. PMID: 40123832 Free PMC article.
-
Hippocampal neurogenesis and Arc expression are enhanced in high-fat fed prepubertal female pigs by a diet including omega-3 fatty acids and Bifidobacterium breve CECT8242.Eur J Nutr. 2023 Sep;62(6):2463-2473. doi: 10.1007/s00394-023-03165-1. Epub 2023 May 6. Eur J Nutr. 2023. PMID: 37148357 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid droplets in central nervous system and functional profiles of brain cells containing lipid droplets in various diseases.J Neuroinflammation. 2025 Jan 13;22(1):7. doi: 10.1186/s12974-025-03334-5. J Neuroinflammation. 2025. PMID: 39806503 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mou Y., Du Y., Zhou L., Yue J., Hu X., Liu Y., Chen S., Lin X., Zhang G., Xiao H., et al. Gut Microbiota Interact With the Brain Through Systemic Chronic Inflammation: Implications on Neuroin-flammation, Neurodegeneration, and Aging. Front. Immunol. 2022;13:1046. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.796288. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

