Bioactives from Crude Rice Bran Oils Extracted Using Green Technology
- PMID: 36985429
- PMCID: PMC10057060
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28062457
Bioactives from Crude Rice Bran Oils Extracted Using Green Technology
Abstract
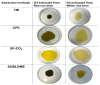
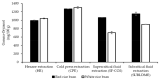
Crude rice bran oils from different rice cultivars and extraction methods bear different contents of nutraceuticals. The health benefits of lowering cholesterol activity of rice bran oil being confirmed by many reports are partly attributed to non-nutrient nutraceuticals, especially γ-oryzanol, phytosterols, and policosanols. As the world has been facing the global warming crisis, green extraction technology is gaining attention from many sectors. The current study aims to compare the nutraceutical composition with respect to γ-oryzanol, phytosterol, and policosanol content as well as the antioxidant properties of crude rice bran oils extracted from white and red rice bran using three green technologies, comparing with conventional hexane extraction. The data show that the traditional solvent extraction gave the highest oil yield percentage (26%), but it was not significantly different from subcritical liquefied dimethyl ether extraction (24.6%). Subcritical liquefied dimethyl ether extraction gave higher oil yield than supercritical CO2 extraction (15.5-16.2%). The crude rice bran oil extracted using subcritical liquefied dimethyl ether extraction produced the highest total phenolic contents and antioxidant activities. The highest γ-oryzanol content of the crude rice bran oil was found in oil extracted by conventional cold press (1370.43 mg/100 g). The γ-oryzanol content of the oil obtained via subcritical liquefied dimethyl ether extraction was high (1213.64 mg/100 g) compared with supercritical CO2 extraction. The red rice bran yielded the crude rice bran oil with the highest total phytosterol content compared with the white bran, and the oil from red rice bran extracted with subcritical liquefied dimethyl ether generated the highest total phytosterol content (1784.17 mg/100 g). The highest policosanol content (274.40 mg/100 g) was also found in oil obtained via subcritical liquefied dimethyl ether extraction.
Keywords: oryzanol; phytosterol; policosanol; subcritical extraction; supercritical extraction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Subcritical dimethyl ether extraction as a simple method to extract nutraceuticals from byproducts from rice bran oil manufacture.Sci Rep. 2020 Dec 3;10(1):21007. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-78011-z. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33273543 Free PMC article.
-
High Levels of Policosanols and Phytosterols from Sugar Mill Waste by Subcritical Liquefied Dimethyl Ether.Foods. 2022 Sep 20;11(19):2937. doi: 10.3390/foods11192937. Foods. 2022. PMID: 36230017 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Extraction Methods on Phytochemicals of Rice Bran Oils Produced from Colored Rice.J Oleo Sci. 2018 Feb 1;67(2):135-142. doi: 10.5650/jos.ess17122. Epub 2018 Jan 23. J Oleo Sci. 2018. PMID: 29367480
-
Rice bran nutraceutics: A comprehensive review.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2017 Nov 22;57(17):3771-3780. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2016.1164120. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2017. PMID: 27015585 Review.
-
Nutrients in rice bran oil and their nutritional functions: a review.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2025;65(14):2840-2857. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2024.2352530. Epub 2024 Jun 10. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2025. PMID: 38856105 Review.
Cited by
-
Phytosterols in rice bran and their health benefits.Front Nutr. 2023 Oct 12;10:1287405. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1287405. eCollection 2023. Front Nutr. 2023. PMID: 37899831 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Surfactant-Free Decellularization of Porcine Auricular Cartilage Using Liquefied Dimethyl Ether and DNase.Materials (Basel). 2023 Apr 18;16(8):3172. doi: 10.3390/ma16083172. Materials (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37110010 Free PMC article.
-
Fatty Acid Esterification of Octacosanol Attenuates Triglyceride and Cholesterol Synthesis in Mice.J Agric Food Chem. 2025 Jan 29;73(4):2430-2442. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.4c10201. Epub 2025 Jan 14. J Agric Food Chem. 2025. PMID: 39808738 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cravotto G., Binello A., Merizzi G., Avogadro M. Improving Solvent-Free Extraction of Policosanol from Rice Bran by High-Intensity Ultrasound Treatment. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2004;106:147–151. doi: 10.1002/ejlt.200300914. - DOI
-
- Krishna A.G.G., Khatoon S., Shiela P.M., Sarmandal C.V., Indira T.N., Mishra A. Effect of Refining of Crude Rice Bran Oil on the Retention of Oryzanol in the Refined Oil. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2001;78:127–131. doi: 10.1007/s11746-001-0232-0. - DOI
-
- Orthoefer F.T. Rice Bran Oil. In: Shahid F., editor. Bailey’s Industrial Oil and Fat Products. Volume 2. John Wiley & Sons, Inc.; Hoboken, NJ, USA: 2005. pp. 465–489.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

