Biofabrication of Functional Pullulan by Aureobasidium pullulans under the Effect of Varying Mineral Salts and Sugar Stress Conditions
- PMID: 36985449
- PMCID: PMC10056076
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28062478
Biofabrication of Functional Pullulan by Aureobasidium pullulans under the Effect of Varying Mineral Salts and Sugar Stress Conditions
Abstract
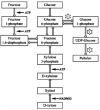
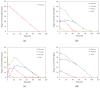
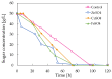
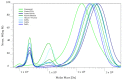
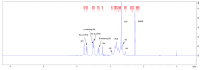
Pullulan is a linear exopolysaccharide, produced in the fermentation media of Aureobasidium pullulans, with a variety of applications in the food and pharmaceutical industries. Pullulan derivatives have growing potential for biomedical applications, but the high cost of pullulan biofabrication currently restricts its commercial use. Better control over pullulan yield, molecular weight and melanin production by altering fermentation conditions could improve the economics. In this study, the effects of sugar and mineral salt stresses on the pullulan production of A. pullulans ATCC 42023 were examined in batch processes. The chemical structure of the recovered pullulan was characterized by FTIR and NMR spectroscopy, and the molecular weight distribution was obtained via SEC. Pullulan yield and melanin production varied when the conditions were adjusted, and pullulans with different molar masses were obtained. Higher-yield pullulan production and a lower polydispersity index were observed when CuSO4 was added to the fermentation in comparison with the control and with the addition of sugars and other salts. Biofabrication of pullulan under stress conditions is a promising strategy to enhance biopolymer yield and to obtain pullulan with a targeted molecular weight.
Keywords: 1H-NMR spectroscopy; FTIR spectroscopy; biofabrication; mineral salt stress; molar mass; pullulan; sugar stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Pandey S., Shreshtha I., Sachan S.G. Pullulan: Biosynthesis, Production and Applications. In: Nadda A.K., Sajna K.V., Sharma S., editors. Microbial Exopolysaccharides as Novel and Significant Biomaterials. 1st ed. Springer; Cham, Switzerland: 2021. pp. 121–141. Chapter 6.
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

