Preparation, Characterization and Evaluation of Flavonolignan Silymarin Effervescent Floating Matrix Tablets for Enhanced Oral Bioavailability
- PMID: 36985575
- PMCID: PMC10054735
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28062606
Preparation, Characterization and Evaluation of Flavonolignan Silymarin Effervescent Floating Matrix Tablets for Enhanced Oral Bioavailability
Abstract
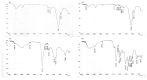
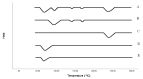
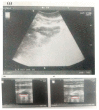
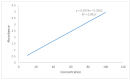
The convenient and highly compliant route for the delivery of active pharmaceutical ingredients is the tablet. A versatile platform of tablets is available for the delivery of therapeutic agents to the gastrointestinal tract. This study aimed to prepare gastro retentive drug delivery floating tablets of silymarin to improve its oral bioavailability and solubility. Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMCK4M and HPMCK15), Carbopol 934p and sodium bicarbonate were used as a matrix, floating enhancer and gas generating agent, respectively. The prepared tablets were evaluated for physicochemical parameters such as hardness, weight variation, friability, floating properties (floating lag time, total floating time), drug content, stability study, in vitro drug release, in vivo floating behavior and in vivo pharmacokinetics. The drug-polymer interaction was studied by Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) thermal analysis and Fourier transform infrared (FTIR). The floating lag time of the formulation was within the prescribed limit (<2 min). The formulation showed good matrix integrity and retarded the release of drug for >12 h. The dissolution can be described by zero-order kinetics (r2 = 0.979), with anomalous diffusion as the release mechanism (n = 0.65). An in vivo pharmacokinetic study showed that Cmax and AUC were increased by up to two times in comparison with the conventional dosage form. An in vivo imaging study showed that the tablet was present in the stomach for 12 h. It can be concluded from this study that the combined matrix system containing hydrophobic and hydrophilic polymers min imized the burst release of the drug from the tablet and achieved a drug release by zero-order kinetics, which is practically difficult with only a hydrophilic matrix. An in vivo pharmacokinetic study elaborated that the bioavailability and solubility of silymarin were improved with an increased mean residence time.
Keywords: effervescent; flavonolignan; floating matrix tablets; oral bioavailability; silymarin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures







References
-
- Kesharwani S.S., Jain V., Dey S., Sharma S., Mallya P., Kumar V.A. An overview of advanced formulation and nanotechnology-based approaches for solubility and bioavailability enhancement of silymarin. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020;60:102021. doi: 10.1016/j.jddst.2020.102021. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

