Microwave Synthesis of Visible-Light-Activated g-C3N4/TiO2 Photocatalysts
- PMID: 36985984
- PMCID: PMC10057508
- DOI: 10.3390/nano13061090
Microwave Synthesis of Visible-Light-Activated g-C3N4/TiO2 Photocatalysts
Abstract
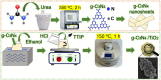
The preparation of visible-light-driven photocatalysts has become highly appealing for environmental remediation through simple, fast and green chemical methods. The current study reports the synthesis and characterization of graphitic carbon nitride/titanium dioxide (g-C3N4/TiO2) heterostructures through a fast (1 h) and simple microwave-assisted approach. Different g-C3N4 amounts mixed with TiO2 (15, 30 and 45 wt. %) were investigated for the photocatalytic degradation of a recalcitrant azo dye (methyl orange (MO)) under solar simulating light. X-ray diffraction (XRD) revealed the anatase TiO2 phase for the pure material and all heterostructures produced. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) showed that by increasing the amount of g-C3N4 in the synthesis, large TiO2 aggregates composed of irregularly shaped particles were disintegrated and resulted in smaller ones, composing a film that covered the g-C3N4 nanosheets. Scanning transmission electron microscopy (STEM) analyses confirmed the existence of an effective interface between a g-C3N4 nanosheet and a TiO2 nanocrystal. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) evidenced no chemical alterations to both g-C3N4 and TiO2 at the heterostructure. The visible-light absorption shift was indicated by the red shift in the absorption onset through the ultraviolet-visible (UV-VIS) absorption spectra. The 30 wt. % of g-C3N4/TiO2 heterostructure showed the best photocatalytic performance, with a MO dye degradation of 85% in 4 h, corresponding to an enhanced efficiency of almost 2 and 10 times greater than that of pure TiO2 and g-C3N4 nanosheets, respectively. Superoxide radical species were found to be the most active radical species in the MO photodegradation process. The creation of a type-II heterostructure is highly suggested due to the negligible participation of hydroxyl radical species in the photodegradation process. The superior photocatalytic activity was attributed to the synergy of g-C3N4 and TiO2 materials.
Keywords: g-C3N4/TiO2; heterostructures; microwave synthesis; photocatalysis; pollutant degradation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures












References
-
- Samsami S., Mohamadi M., Sarrafzadeh M.H., Rene E.R., Firoozbahr M. Recent advances in the treatment of dye-containing wastewater from textile industries: Overview and perspectives. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2020;143:138–163. doi: 10.1016/j.psep.2020.05.034. - DOI
-
- Al-Tohamy R., Ali S.S., Li F., Okasha K.M., Mahmoud Y.A.G., Elsamahy T., Jiao H., Fu Y., Sun J. A critical review on the treatment of dye-containing wastewater: Ecotoxicological and health concerns of textile dyes and possible remediation approaches for environmental safety. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022;231:113160. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.113160. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Aich V., Ehlert K., editors. Global Water Partnership and World Meteorological Organization. WMO; Geneva, Switzerland: 2022. Drought and Water Scarcity; pp. 1–24.
Grants and funding
- UI/BD/151292/2021 (Ph.D. research scholarship), LA/P/0037/2020, UIDP/50025/2020, and UIDB/50025/2020 of the Associate Laboratory Institute of Nanostructures, Nanomodelling, and Nanofabrication-i3N, but also the 2021.03825.CEECIND/Fundação para a Ciência e Tecnologia
- H2020 program under grant agreement No. 787410 (ERC-2018-AdG DIGISMART)/European Council
- EC project SYNERGY H2020-WIDESPREAD-2020-5, CSA, proposal nº 952169, EMERGE-2020-INFRAIA-2020-1, proposal nº 101008701/European Council
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

