Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase (G6PD) Measurement Using Biosensors by Community-Based Village Malaria Workers and Hospital Laboratory Staff in Cambodia: A Quantitative Study
- PMID: 36986323
- PMCID: PMC10056797
- DOI: 10.3390/pathogens12030400
Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase (G6PD) Measurement Using Biosensors by Community-Based Village Malaria Workers and Hospital Laboratory Staff in Cambodia: A Quantitative Study
Abstract
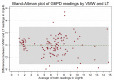
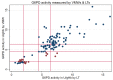
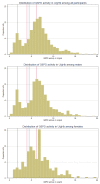
Vivax malaria can relapse after an initial infection due to dormant liver stages of the parasite. Radical cure can prevent relapses but requires the measurement of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase enzyme (G6PD) activity to identify G6PD-deficient patients at risk of drug-induced haemolysis. In the absence of reliable G6PD testing, vivax patients are denied radical curative treatment in many places, including rural Cambodia. A novel Biosensor, 'G6PD Standard' (SD Biosensor, Republic of Korea; Biosensor), can measure G6PD activity at the point of care. The objectives of this study were to compare the G6PD activity readings using Biosensors by village malaria workers (VMWs) and hospital-based laboratory technicians (LTs), and to compare the G6PD deficiency categorization recommended by the Biosensor manufacturer with categories derived from a locally estimated adjusted male median (AMM) in Kravanh district, Cambodia. Participants were enrolled between 2021 and 2022 in western Cambodia. Each of the 28 VMWs and 5 LTs received a Biosensor and standardized training on its use. The G6PD activities of febrile patients identified in the community were measured by VMWs; in a subset, a second reading was done by LTs. All participants were tested for malaria by rapid diagnostic test (RDT). The adjusted male median (AMM) was calculated from all RDT-negative participants and defined as 100% G6PD activity. VMWs measured activities in 1344 participants. Of that total, 1327 (98.7%) readings were included in the analysis, and 68 of these had a positive RDT result. We calculated 100% activity as 6.4 U/gHb (interquartile range: 4.5 to 7.8); 9.9% (124/1259) of RDT-negative participants had G6PD activities below 30%, 15.2% (191/1259) had activities between 30% and 70%, and 75.0% (944/1259) had activities greater than 70%. Repeat measurements among 114 participants showed a significant correlation of G6PD readings (rs = 0.784, p < 0.001) between VMWs and LTs. Based on the manufacturer's recommendations, 285 participants (21.5%) had less than 30% activity; however, based on the AMM, 132 participants (10.0%) had less than 30% activity. The G6PD measurements by VMWs and LTs were similar. With the provisions of training, supervision, and monitoring, VMWs could play an important role in the management of vivax malaria, which is critical for the rapid elimination of malaria regionally. Definitions of deficiency based on the manufacturer's recommendations and the population-specific AMM differed significantly, which may warrant revision of these recommendations.
Keywords: G6PD; Southeast Asia; biosensor; primaquine; radical cure; village malaria worker; vivax malaria.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization (WHO) Accelerating Malaria Elimination in the Greater Mekong. 2022. [(accessed on 17 March 2022)]. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/rest/bitstreams/1413368/retrieve.
-
- Clinton Health Initiative (CHAI) G6PD Testing in Cambodia and Laos—Piloting and Implementation. 2020. [(accessed on 27 July 2022)]. Available online: https://www.vivaxmalaria.org/sites/p-vivax/files/content/attachments/202....
-
- Centre National de Malariologie (CNM) Malaria Infiormation System. [(accessed on 18 June 2022)];2022 Available online: https://mis.cnm.gov.kh/
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

