Combined Toxicity of the Most Common Indoor Aspergilli
- PMID: 36986381
- PMCID: PMC10058518
- DOI: 10.3390/pathogens12030459
Combined Toxicity of the Most Common Indoor Aspergilli
Abstract
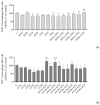
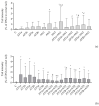
The most common Aspergilli isolated from indoor air samples from occupied buildings and a grain mill were extracted and analyzed for their combined (Flavi + Nigri, Versicolores + Nigri) cytotoxic, genotoxic and pro-inflammatory properties on human adenocarcinoma cells (A549) and monocytic leukemia cells induced in macrophages (THP-1 macrophages). Metabolite mixtures from the Aspergilli series Nigri increase the cytotoxic and genotoxic potency of Flavi extracts in A549 cells suggesting additive and/or synergistic effects, while antagonizing the cytotoxic potency of Versicolores extracts in THP-1 macrophages and genotoxicity in A549 cells. All tested combinations significantly decreased IL-5 and IL-17, while IL-1β, TNF-α and IL-6 relative concentrations were increased. Exploring the toxicity of extracted Aspergilli deepens the understanding of intersections and interspecies differences in events of chronic exposure to their inhalable mycoparticles.
Keywords: cytotoxicity; genotoxicity; proinflammatory cytokines; section Flavi; series Nigri; series Versicolores.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- WHO . Guidelines for Indoor Air Quality and Dampness. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2010.
-
- Piecková E., Jesenská Z. Microscopic Fungi in Dwellings and Their Health Implications in Humans. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 1999;6:1–11. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

