Kinin B1 and B2 Receptors Contribute to Cisplatin-Induced Painful Peripheral Neuropathy in Male Mice
- PMID: 36986713
- PMCID: PMC10051506
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15030852
Kinin B1 and B2 Receptors Contribute to Cisplatin-Induced Painful Peripheral Neuropathy in Male Mice
Abstract
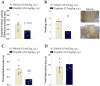
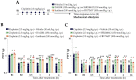
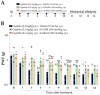
Cisplatin is the preferential chemotherapeutic drug for highly prevalent solid tumours. However, its clinical efficacy is frequently limited due to neurotoxic effects such as peripheral neuropathy. Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy is a dose-dependent adverse condition that negatively impacts quality of life, and it may determine dosage limitations or even cancer treatment cessation. Thus, it is urgently necessary to identify pathophysiological mechanisms underlying these painful symptoms. As kinins and their B1 and B2 receptors contribute to the development of chronic painful conditions, including those induced by chemotherapy, the contribution of these receptors to cisplatin-induced peripheral neuropathy was evaluated via pharmacological antagonism and genetic manipulation in male Swiss mice. Cisplatin causes painful symptoms and impaired working and spatial memory. Kinin B1 (DALBK) and B2 (Icatibant) receptor antagonists attenuated some painful parameters. Local administration of kinin B1 and B2 receptor agonists (in sub-nociceptive doses) intensified the cisplatin-induced mechanical nociception attenuated by DALBK and Icatibant, respectively. In addition, antisense oligonucleotides to kinin B1 and B2 receptors reduced cisplatin-induced mechanical allodynia. Thus, kinin B1 and B2 receptors appear to be potential targets for the treatment of cisplatin-induced painful symptoms and may improve patients' adherence to treatment and their quality of life.
Keywords: CIPN; allodynia; bradykinin; chemotherapy; neuropathic pain.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Kerns S.L., Fung C., Monahan P.O., Ardeshir-Rouhani-Fard S., Abu Zaid M.I., Williams A.L.M., Stump T.E., Sesso H.D., Feldman D.R., Hamilton R.J., et al. Cumulative Burden of Morbidity among Testicular Cancer Survivors after Standard Cisplatin-Based Chemotherapy: A Multi-Institutional Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018;36:1505–1512. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2017.77.0735. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Travis L.B., Fossa S.D., Sesso H.D., Frisina R.D., Herrmann D.N., Beard C.J., Feldman D.R., Pagliaro L.C., Miller R.C., Vaughn D.J., et al. Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neurotoxicity and Ototoxicity: New Paradigms for Translational Genomics. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2014;106:dju044. doi: 10.1093/jnci/dju044. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
- #21/2551-0001966-2/Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado do Rio Grande do Sul
- #304985/2020-1/National Council for Scientific and Technological Development
- process #23038.002125/2021-85; Grant: #0036/2021/Coordenação de Aperfeicoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior
- #88887.568915/2020-00/Coordenação de Aperfeicoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior
- #88882.182170/2018-01/Coordenação de Aperfeicoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

