Evaluations of Andrographolide-Rich Fractions of Andrographis paniculata with Enhanced Potential Antioxidant, Anticancer, Antihypertensive, and Anti-Inflammatory Activities
- PMID: 36986909
- PMCID: PMC10052505
- DOI: 10.3390/plants12061220
Evaluations of Andrographolide-Rich Fractions of Andrographis paniculata with Enhanced Potential Antioxidant, Anticancer, Antihypertensive, and Anti-Inflammatory Activities
Abstract
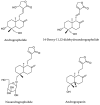
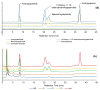
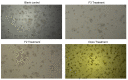
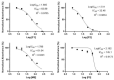
Andrographis paniculata is widely used as a traditional medicine in Asian countries. It has been classified as a safe and non-toxic medicine by traditional Chinese medicine. The investigation of the biological activities of A. paniculata is still focused on the crude extract and isolation of its main active compound, andrographolide, and its derivatives. However, the use of andrographolide alone has been shown to exacerbate unwanted effects. This highlights the importance of developing a fraction of A. paniculata with enhanced efficacy as an herbal-based medicine. In this study, the extraction and fractionation of A. paniculata, followed by quantitative analysis using high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with a DAD detector, were established to quantify the andrographolide and its derivative in each fraction. Biological activities, such as antioxidant, anticancer, antihypertensive, and anti-inflammatory activities, were evaluated to study their correlations with the quantification of active substances of A. paniculata extract and its fractions. The 50% methanolic fraction of A. paniculata exhibited the best cytotoxic activities against CACO-2 cells, as well as the best anti-inflammatory and antihypertensive activities compared to other extracts. The 50% methanolic fraction also displayed the highest quantification of its main active compound, andrographolide, and its derivatives, 14-deoxy-11,12-didehydroandrographolide, neoandrographolide, and andrograpanin, among others.
Keywords: Andrographis paniculata; andrographolide; anti-inflammatory; anticancer; antihypertensive; antioxidant; traditional Chinese medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
All the authors declare no conflict of interest regarding this work.
Figures

References
-
- Saxena R.C., Singh R., Kumar P., Yadav S.C., Negi M.P.S., Saxena V.S., Joshua A.J., Vijayabalaji V., Goudar K.S., Venkateshwarlu K., et al. A Randomized Double Blind Placebo Controlled Clinical Evaluation of Extract of Andrographis paniculata (KalmCold™) in Patients with Uncomplicated Upper Respiratory Tract Infection. Phytomedicine. 2010;17:178–185. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2009.12.001. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Barua P.M.B., Sahu P.R., Mondal E., Bose G., Khan A.T. A Mild and Environmentally Benign Synthetic Protocol for Catalytic Hydrolysis of Thioglycosides. Synlett. 2002;2002:0081–0084. doi: 10.1055/s-2002-19340. - DOI
-
- Marcos I., Pedrero A., Sexmero M., Diez D., Basabe P., Hernández F., Urones J. Synthesis and Absolute Configuration of Three Natural Ent-Halimanolides with Biological Activity. Tetrahedron Lett. 2003;44:369–372. doi: 10.1016/S0040-4039(02)02535-2. - DOI
-
- Siedle B., García-Piñeres A.J., Murillo R., Schulte-Mönting J., Castro V., Rüngeler P., Klaas C.A., Da Costa F.B., Kisiel W., Merfort I. Quantitative Structure–Activity Relationship of Sesquiterpene Lactones as Inhibitors of the Transcription Factor NF-ΚB. J. Med. Chem. 2004;47:6042–6054. doi: 10.1021/jm049937r. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

