Small Talk: On the Possible Role of Trans-Kingdom Small RNAs during Plant-Virus-Vector Tritrophic Communication
- PMID: 36987098
- PMCID: PMC10059270
- DOI: 10.3390/plants12061411
Small Talk: On the Possible Role of Trans-Kingdom Small RNAs during Plant-Virus-Vector Tritrophic Communication
Abstract
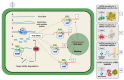
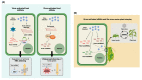
Small RNAs (sRNAs) are the hallmark and main effectors of RNA silencing and therefore are involved in major biological processes in plants, such as regulation of gene expression, antiviral defense, and plant genome integrity. The mechanisms of sRNA amplification as well as their mobile nature and rapid generation suggest sRNAs as potential key modulators of intercellular and interspecies communication in plant-pathogen-pest interactions. Plant endogenous sRNAs can act in cis to regulate plant innate immunity against pathogens, or in trans to silence pathogens' messenger RNAs (mRNAs) and impair virulence. Likewise, pathogen-derived sRNAs can act in cis to regulate expression of their own genes and increase virulence towards a plant host, or in trans to silence plant mRNAs and interfere with host defense. In plant viral diseases, virus infection alters the composition and abundance of sRNAs in plant cells, not only by triggering and interfering with the plant RNA silencing antiviral response, which accumulates virus-derived small interfering RNAs (vsiRNAs), but also by modulating plant endogenous sRNAs. Here, we review the current knowledge on the nature and activity of virus-responsive sRNAs during virus-plant interactions and discuss their role in trans-kingdom modulation of virus vectors for the benefit of virus dissemination.
Keywords: Small RNA-based communication; plant viral diseases; plant viruses; trans-kingdom RNA silencing; virus–plant interactions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Virus and Viroid-Derived Small RNAs as Modulators of Host Gene Expression: Molecular Insights Into Pathogenesis.Front Microbiol. 2021 Jan 14;11:614231. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.614231. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33584579 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Systemic silencing of an endogenous plant gene by two classes of mobile 21-nucleotide artificial small RNAs.Plant J. 2022 May;110(4):1166-1181. doi: 10.1111/tpj.15730. Epub 2022 Mar 27. Plant J. 2022. PMID: 35277899 Free PMC article.
-
Diverse Functions of Small RNAs in Different Plant-Pathogen Communications.Front Microbiol. 2016 Oct 4;7:1552. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.01552. eCollection 2016. Front Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27757103 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biogenesis, Function, and Applications of Virus-Derived Small RNAs in Plants.Front Microbiol. 2015 Nov 9;6:1237. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2015.01237. eCollection 2015. Front Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 26617580 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent advances in small RNA mediated plant-virus interactions.Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2019 Jun;39(4):587-601. doi: 10.1080/07388551.2019.1597830. Epub 2019 Apr 4. Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 30947560 Review.
Cited by
-
A viral small interfering RNA-host plant mRNA pathway modulates virus-induced drought tolerance by enhancing autophagy.Plant Cell. 2024 Sep 3;36(9):3219-3236. doi: 10.1093/plcell/koae158. Plant Cell. 2024. PMID: 38801738 Free PMC article.
-
Aphids on Aphid-Susceptible Cultivars Have Easy Access to Turnip Mosaic Virus, and Effective Inoculation on Aphid-Resistant Cultivars of Oilseed Rape (Brassica napus).Plants (Basel). 2023 May 13;12(10):1972. doi: 10.3390/plants12101972. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37653889 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

