Synergistic Effects of Water Management and Silicon Foliar Spraying on the Uptake and Transport Efficiency of Cadmium in Rice (Oryza sativa L.)
- PMID: 36987102
- PMCID: PMC10053962
- DOI: 10.3390/plants12061414
Synergistic Effects of Water Management and Silicon Foliar Spraying on the Uptake and Transport Efficiency of Cadmium in Rice (Oryza sativa L.)
Abstract
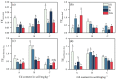
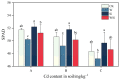
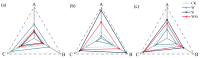
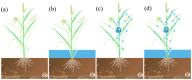
To study the synergistic effects of water management and silicon (Si) foliar spraying on the uptake and transport of cadmium (Cd) in rice, we designed four treatments: conventional intermittent flooding + no Si foliar spraying (CK), continuous flooding throughout the growth stage + no Si foliar spraying (W), conventional intermittent flooding + Si foliar spraying (Si) and continuous flooding throughout the growth stage + Si foliar spraying (WSi). The results show that WSi treatment reduced the uptake and translocation of Cd by rice and significantly reduced the brown rice Cd content, with no effect on rice yield. Compared with CK, the Si treatment increased the net photosynthetic rate (Pn), stomatal conductance (Gs) and transpiration rate (Tr) of rice by 6.5-9.4%, 10.0-16.6% and 2.1-16.8%, respectively. The W treatment decreased these parameters by 20.5-27.9%, 8.6-26.8% and 13.3-23.3%, respectively, and the WSi treatment decreased them by 13.1-21.2%, 3.7-22.3% and 2.2-13.7%, respectively. The superoxide dismutase (SOD) and peroxidase (POD) activity decreased by 6.7-20.6% and 6.5-9.5%, respectively, following the W treatment. Following the Si treatment, SOD and POD activity increased by 10.2-41.1% and 9.3-25.1%, respectively, and following the WSi treatment, they increased by 6.5-18.1% and 2.6-22.4%, respectively. Si foliar spraying ameliorated the detrimental effects of continuous flooding throughout the growth stage on photosynthesis and antioxidant enzyme activity. We conclude that synergistic continuous flooding throughout the growth stage, combined with Si foliar spraying, can significantly block Cd uptake and translocation and is therefore an effective means of reducing the accumulation of Cd in brown rice.
Keywords: Si; cadmium; foliar spraying; photosynthesis; water management.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Effect of silicon spraying on rice photosynthesis and antioxidant defense system on cadmium accumulation.Sci Rep. 2024 Jul 3;14(1):15265. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-66204-9. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38961133 Free PMC article.
-
Foliar spraying with silicon and selenium reduces cadmium uptake and mitigates cadmium toxicity in rice.Sci Total Environ. 2018 Aug 1;631-632:1100-1108. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.03.047. Epub 2018 Mar 16. Sci Total Environ. 2018. PMID: 29727936
-
Co-application of water management and foliar spraying silicon to reduce cadmium and arsenic uptake in rice: A two-year field experiment.Sci Total Environ. 2022 Apr 20;818:151801. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.151801. Epub 2021 Nov 19. Sci Total Environ. 2022. PMID: 34801493
-
Cadmium uptake reduction in paddy rice with a combination of water management, soil application of calcium magnesium phosphate and foliar spraying of Si/Se.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2021 Sep;28(36):50378-50387. doi: 10.1007/s11356-021-13512-6. Epub 2021 May 6. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2021. PMID: 33956320
-
Silicon application improved the yield and nutritional quality while reduced cadmium concentration in rice.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2020 Jun;27(16):20370-20379. doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-08357-4. Epub 2020 Apr 2. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2020. PMID: 32240508
Cited by
-
Comparing the Effects of Lime Soil and Yellow Soil on Cadmium Accumulation in Rice during Grain-Filling and Maturation Periods.Plants (Basel). 2024 Jul 23;13(15):2018. doi: 10.3390/plants13152018. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39124137 Free PMC article.
-
Ameliorating Effects of Graphene Oxide on Cadmium Accumulation and Eco-Physiological Characteristics in a Greening Hyperaccumulator (Lonicera japonica Thunb.).Plants (Basel). 2023 Dec 20;13(1):19. doi: 10.3390/plants13010019. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38202327 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Cadmium Stress on Carbon Sequestration and Oxygen Release Characteristics in A Landscaping Hyperaccumulator-Lonicera japonica Thunb.Plants (Basel). 2023 Jul 19;12(14):2689. doi: 10.3390/plants12142689. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37514303 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of common horsetail extract on growth characteristics, essential oil yield and chemical compositions of basil (Ocimum basilicum L.).Sci Rep. 2024 May 15;14(1):11082. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-61830-9. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38744893 Free PMC article.
-
An Overview of the Mechanisms through Which Plants Regulate ROS Homeostasis under Cadmium Stress.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Sep 26;13(10):1174. doi: 10.3390/antiox13101174. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39456428 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

