Cyclodextrin-Based Polymeric Drug Delivery Systems for Cancer Therapy
- PMID: 36987181
- PMCID: PMC10052104
- DOI: 10.3390/polym15061400
Cyclodextrin-Based Polymeric Drug Delivery Systems for Cancer Therapy
Abstract
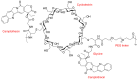
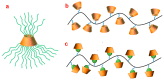
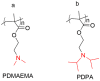
Cyclodextrins (CDs) are one of the most extensively studied cyclic-oligosaccharides due to their low toxicity, good biodegradability and biocompatibility, facile chemical modification, and unique inclusion capacity. However, problems such as poor pharmacokinetics, plasma membrane disruption, hemolytic effects and a lack of target specificity still exist for their applications as drug carriers. Recently, polymers have been introduced into CDs to combine the advantages of both biomaterials for the superior delivery of anticancer agents in cancer treatment. In this review, we summarize four types of CD-based polymeric carriers for the delivery of chemotherapeutics or gene agents for cancer therapy. These CD-based polymers were classified based on their structural properties. Most of the CD-based polymers were amphiphilic with the introduction of hydrophobic/hydrophilic segments and were able to form nanoassemblies. Anticancer drugs could be included in the cavity of CDs, encapsulated in the nanoparticles or conjugated on the CD-based polymers. In addition, the unique structures of CDs enable the functionalization of targeting agents and stimuli-responsive materials to realize the targeting and precise release of anticancer agents. In summary, CD-based polymers are attractive carriers for anticancer agents.
Keywords: conjugate; copolymer; crosslink; cyclodextrin; polymer; polyrotaxane.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


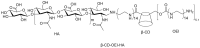
Similar articles
-
Cyclodextrin-based supramolecular architectures: syntheses, structures, and applications for drug and gene delivery.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2008 Jun 10;60(9):1000-17. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2008.02.011. Epub 2008 Mar 4. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2008. PMID: 18413280 Review.
-
Multifunctionality of cyclodextrin-based polymeric nanoparticulate delivery systems for chemotherapeutics, combination therapy, and theranostics.Int J Pharm. 2024 Apr 10;654:123976. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2024.123976. Epub 2024 Mar 6. Int J Pharm. 2024. PMID: 38452831 Review.
-
Role of Cyclodextrins in Nanoparticle-Based Drug Delivery Systems.J Pharm Sci. 2018 Jul;107(7):1741-1753. doi: 10.1016/j.xphs.2018.03.021. Epub 2018 Apr 3. J Pharm Sci. 2018. PMID: 29625157 Review.
-
Cyclodextrin-based delivery systems for chemotherapeutic anticancer drugs: A review.Carbohydr Polym. 2020 Mar 15;232:115805. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.115805. Epub 2019 Dec 30. Carbohydr Polym. 2020. PMID: 31952603 Review.
-
Cyclodextrin-based host-guest supramolecular nanoparticles for delivery: from design to applications.Acc Chem Res. 2014 Jul 15;47(7):2017-25. doi: 10.1021/ar500055s. Epub 2014 May 29. Acc Chem Res. 2014. PMID: 24873201
Cited by
-
Chitosan and Cyclodextrins-Versatile Materials Used to Create Drug Delivery Systems for Gastrointestinal Cancers.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Dec 27;16(1):43. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16010043. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 38258054 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DFT Study of Interaction between Teriflunomide and β-cyclodextrin.Curr Mol Med. 2025;25(2):187-201. doi: 10.2174/0115665240270161231112120838. Curr Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 38243924
-
Solubilization techniques used for poorly water-soluble drugs.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2024 Nov;14(11):4683-4716. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2024.08.027. Epub 2024 Sep 2. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2024. PMID: 39664427 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Preparation and Characterization of Fenofibrate-Loaded Fibers Based on 2-Hydroxylpropyl-β-Cyclodextrin.Polymers (Basel). 2025 Apr 11;17(8):1037. doi: 10.3390/polym17081037. Polymers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40284304 Free PMC article.
-
Extraction and comparison of the interactions of tetracycline antibiotics by different types of cyclodextrins using molecular docking studies.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 21;15(1):26431. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-04120-2. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40691681 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Braga S.S. Cyclodextrin superstructures for drug delivery. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2022;75:103650. doi: 10.1016/j.jddst.2022.103650. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

