Coating Methods of Carbon Nonwovens with Cross-Linked Hyaluronic Acid and Its Conjugates with BMP Fragments
- PMID: 36987331
- PMCID: PMC10054264
- DOI: 10.3390/polym15061551
Coating Methods of Carbon Nonwovens with Cross-Linked Hyaluronic Acid and Its Conjugates with BMP Fragments
Abstract
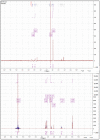
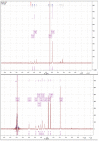
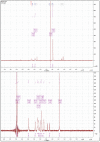
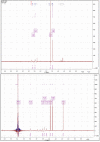
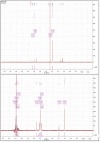
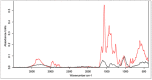
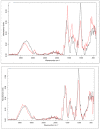
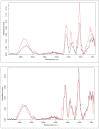
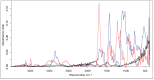
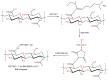
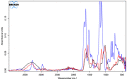
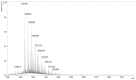
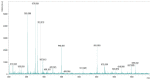
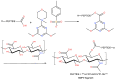
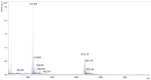
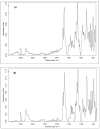
The cross-linking of polysaccharides is a universal approach to affect their structure and physical properties. Both physical and chemical methods are used for this purpose. Although chemical cross-linking provides good thermal and mechanical stability for the final products, the compounds used as stabilizers can affect the integrity of the cross-linked substances or have toxic properties that limit the applicability of the final products. These risks might be mitigated by using physically cross-linked gels. In the present study, we attempted to obtain hybrid materials based on carbon nonwovens with a layer of cross-linked hyaluronan and peptides that are fragments of bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs). A variety of cross-linking procedures and cross-linking agents (1,4-butanediamine, citric acid, and BDDE) were tested to find the most optimal method to coat the hydrophobic carbon nonwovens with a hydrophilic hyaluronic acid (HA) layer. Both the use of hyaluronic acid chemically modified with BMP fragments and a physical modification approach (layer-by-layer method) were proposed. The obtained hybrid materials were tested with the spectrometric (MALDI-TOF MS) and spectroscopic methods (IR and 1H-NMR). It was found that the chemical cross-linking of polysaccharides is an effective method for the deposition of a polar active substance on the surface of a hydrophobic carbon nonwoven fabric and that the final material is highly biocompatible.
Keywords: BDDE; BMP fragments; carbon nonwoven; citric acid; coating; cross-linking; hyaluronic acid.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Wang W., Liu Y., Xie Z. Gecko-Like Dry Adhesive surfaces and their applications: A review. J. Bionic Eng. 2021;18:1011–1044. doi: 10.1007/s42235-021-00088-7. - DOI
-
- Kim B.S., Kim M.K., Cho Y., Hamed E.E., Gillette M.U., Cha H., Miljkovic N., Aakalu V.K., Kang K., Son K.-N., et al. Electrothermal soft manipulator enabling safe transport and handling of thin cell/tissue sheets and bioelectronic devices. Sci. Adv. 2020;6:42. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abc5630. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Weissmann B., Meyer K. The structure of hyaluronic acid and of hyaluronic acid from umbilical cord. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1954;76:1753–1757. doi: 10.1021/ja01636a010. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

