Dental MRI-only a future vision or standard of care? A literature review on current indications and applications of MRI in dentistry
- PMID: 36988090
- PMCID: PMC10170172
- DOI: 10.1259/dmfr.20220333
Dental MRI-only a future vision or standard of care? A literature review on current indications and applications of MRI in dentistry
Abstract
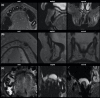
MRI is increasingly used as a diagnostic tool for visualising the dentoalveolar complex. A comprehensive review of the current indications and applications of MRI in the dental specialities of orthodontics (I), endodontics (II), prosthodontics (III), periodontics (IV), and oral surgery (V), pediatric dentistry (VI), operative dentistry is still missing and is therefore provided by the present work.The current literature on dental MRI shows that it is used for cephalometry in orthodontics and dentofacial orthopaedics, detection of dental pulp inflammation, characterisation of periapical and marginal periodontal pathologies of teeth, caries detection, and identification of the inferior alveolar nerve, impacted teeth and dentofacial anatomy for dental implant planning, respectively. Specific protocols regarding the miniature anatomy of the dentofacial complex, the presence of hard tissues, and foreign body restorations are used along with dedicated coils for the improved image quality of the facial skull.Dental MRI poses a clinically useful radiation-free imaging tool for visualising the dentoalveolar complex across dental specialities when respecting the indications and limitations.
Keywords: Dentistry; Diagnostic Imaging; Magnetic Resonance Imaging.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

