Synthetic ERRα/β/γ Agonist Induces an ERRα-Dependent Acute Aerobic Exercise Response and Enhances Exercise Capacity
- PMID: 36988910
- PMCID: PMC11584170
- DOI: 10.1021/acschembio.2c00720
Synthetic ERRα/β/γ Agonist Induces an ERRα-Dependent Acute Aerobic Exercise Response and Enhances Exercise Capacity
Abstract
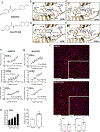
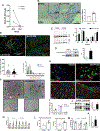
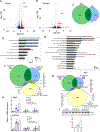
Repetitive physical exercise induces physiological adaptations in skeletal muscle that improves exercise performance and is effective for the prevention and treatment of several diseases. Genetic evidence indicates that the orphan nuclear receptors estrogen receptor-related receptors (ERRs) play an important role in skeletal muscle exercise capacity. Three ERR subtypes exist (ERRα, β, and γ), and although ERRβ/γ agonists have been designed, there have been significant difficulties in designing compounds with ERRα agonist activity. Additionally, there are limited synthetic agonists that can be used to target ERRs in vivo. Here, we report the identification of a synthetic ERR pan agonist, SLU-PP-332, that targets all three ERRs but has the highest potency for ERRα. Additionally, SLU-PP-332 has sufficient pharmacokinetic properties to be used as an in vivo chemical tool. SLU-PP-332 increases mitochondrial function and cellular respiration in a skeletal muscle cell line. When administered to mice, SLU-PP-332 increased the type IIa oxidative skeletal muscle fibers and enhanced exercise endurance. We also observed that SLU-PP-332 induced an ERRα-specific acute aerobic exercise genetic program, and the ERRα activation was critical for enhancing exercise endurance in mice. These data indicate the feasibility of targeting ERRα for the development of compounds that act as exercise mimetics that may be effective in the treatment of numerous metabolic disorders and to improve muscle function in the aging.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following competing financial interest(s): T.P.B., B.E., and J.K.W. are stockholders in Myonid Therapeutics, Inc., which focuses on ERR based therapeutics.
Figures

References
-
- O’Gorman DJ; Karlsson HK; McQuaid S; Yousif O; Rahman Y; Gasparro D; Glund S; Chibalin AV; Zierath JR; Nolan JJ Exercise training increases insulin-stimulated glucose disposal and GLUT4 (SLC2A4) protein content in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 2006, 49, 2983–2992. - PubMed
-
- Koopman R; Manders RJ; Zorenc AH; Hul GB; Kuipers H; Keizer HA; van Loon LJ A single session of resistance exercise enhances insulin sensitivity for at least 24 h in healthy men. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol 2005, 94, 180–187. - PubMed
-
- Borsheim E; Bahr R Effect of exercise intensity, duration and mode on post-exercise oxygen consumption. Sports Med 2003, 33, 1037–1060. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

