Ultralow-dose binary oncolytic/helper-dependent adenovirus promotes antitumor activity in preclinical and clinical studies
- PMID: 36989357
- PMCID: PMC10058234
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.ade6790
Ultralow-dose binary oncolytic/helper-dependent adenovirus promotes antitumor activity in preclinical and clinical studies
Abstract
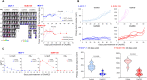
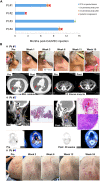
We show that a binary oncolytic/helper-dependent adenovirus (CAdVEC) that both lyses tumor cells and locally expresses the proinflammatory cytokine IL-12 and PD-L1 blocking antibody has potent antitumor activity in humanized mouse models. On the basis of these preclinical studies, we treated four patients with a single intratumoral injection of an ultralow dose of CAdVEC (NCT03740256), representing a dose of oncolytic adenovirus more than 100-fold lower than used in previous trials. While CAdVEC caused no significant toxicities, it repolarized the tumor microenvironment with increased infiltration of CD8 T cells. A single administration of CAdVEC was associated with both locoregional and abscopal effects on metastases and, in combination with systemic administration of immune checkpoint antibodies, induced sustained antitumor responses, including one complete and two partial responses. Hence, in both preclinical and clinical studies, CAdVEC is safe and even at extremely low doses is sufficiently potent to induce significant tumor control through oncolysis and immune repolarization.
Figures




References
-
- M. Yamada, T. Mizuno, J. Yamaguchi, Y. Yokoyama, T. Igami, S. Onoe, N. Watanabe, K. Uehara, K. Matsuo, T. Ebata, Superiority of clinical American Joint Committee on Cancer T classification for perihilar cholangiocarcinoma. J. Hepatobiliary Pancreat. Sci. 29, 768–777 (2021). - PubMed
-
- K. Harrington, D. J. Freeman, B. Kelly, J. Harper, J.-C. Soria, Optimizing oncolytic virotherapy in cancer treatment. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 18, 689–706 (2019). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

