Aberrant cell state plasticity mediated by developmental reprogramming precedes colorectal cancer initiation
- PMID: 36989360
- PMCID: PMC10058311
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adf0927
Aberrant cell state plasticity mediated by developmental reprogramming precedes colorectal cancer initiation
Abstract
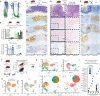
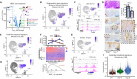
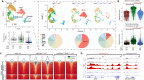
Cell state plasticity is carefully regulated in adult epithelia to prevent cancer. The aberrant expansion of the normally restricted capability for cell state plasticity in neoplasia is poorly defined. Using genetically engineered and carcinogen-induced mouse models of intestinal neoplasia, we observed that impaired differentiation is a conserved event preceding cancer development. Single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) of premalignant lesions from mouse models and a patient with hereditary polyposis revealed that cancer initiates by adopting an aberrant transcriptional state characterized by regenerative activity, marked by Ly6a (Sca-1), and reactivation of fetal intestinal genes, including Tacstd2 (Trop2). Genetic inactivation of Sox9 prevented adenoma formation, obstructed the emergence of regenerative and fetal programs, and restored multilineage differentiation by scRNA-seq. Expanded chromatin accessibility at regeneration and fetal genes upon Apc inactivation was reduced by concomitant Sox9 suppression. These studies indicate that aberrant cell state plasticity mediated by unabated regenerative activity and developmental reprogramming precedes cancer development.
Figures




References
-
- F. de Sousa E Melo, F. J. de Sauvage, Cellular plasticity in intestinal homeostasis and disease. Cell Stem Cell 24, 54–64 (2019). - PubMed
-
- D. Shlyueva, G. Stampfel, A. Stark, Transcriptional enhancers: From properties to genome-wide predictions. Nat. Rev. Genet. 15, 272–286 (2014). - PubMed
-
- I. Arozarena, C. Wellbrock, Phenotype plasticity as enabler of melanoma progression and therapy resistance. Nat. Rev. Cancer 19, 377–391 (2019). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

